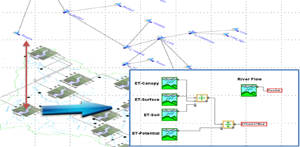
To better understand how natural systems react to changing conditions, environmentalists have turned to simulation to help establish appropriate policy and make informed decisions.

Dam
Raising
ExtendSim Consultant Ben Twomey has found that using ExtendSim for dynamic simulation to solve some types of problems can be a very fast solution. Eight hours was all that was needed to build and deliver a two-site dam raising simulation that estimated completion schedule as a function of shift structure, hauler selection, and more. ExtendSim provided Ben "robust, rapid decision support that a spreadsheet couldn't deliver".
An energetic materials environmental study was completed with participation from NASA, the Environmental Protection Agency, and others to define the environmental impact of energetic materials waste (gun propellant). The ExtendSim model developed by The Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (SERDP) documented environmental cost information such as cost for waste, air emissions, permitting, and pollution prevention to help establish a standard for the development of new energetic materials.
Using Extendsim, Savannah River National Lab developed simulation models of the Savannah River Site. These models examine the process plutonium and spent uranium fuel rods undergo as they are being turned into waste and/or mixed oxide fuels.
ExtendSim and the Environment
- System design for wastewater treatment for rural and low-income disadvantaged communities.
- Environmental impact analysis of construction projects.
- Predicting the impact of R&D and capital investment decisions on the evolution of biomass conversion technologies for feedstock development.
- Sustainability and traceability.
- Predict future weather patterns.
- Trading and marketing strategies for recycled glass.
Who is Using ExtendSim
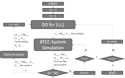 Researchers created a prototype simulation-based optimization (SIMOPT) approach to study the biomass to commodity chemicals (BTCC) system evolution under exogenous and endogenous uncertainties. The model provides a preliminary analysis of the impact of using three different sampling methods, i.e., Monte Carlo, Latin Hypercube, and Halton sequence, to generate simulation runs to achieve the least computational cost of the SIMOPT approach to reach a statistically significant solution.
Researchers created a prototype simulation-based optimization (SIMOPT) approach to study the biomass to commodity chemicals (BTCC) system evolution under exogenous and endogenous uncertainties. The model provides a preliminary analysis of the impact of using three different sampling methods, i.e., Monte Carlo, Latin Hypercube, and Halton sequence, to generate simulation runs to achieve the least computational cost of the SIMOPT approach to reach a statistically significant solution.- ExtendSim was used to devise a treatment alternative evaluation for the City of Phoenix Western Canal Well Field Study to help optimize planning, design, and operational parameters.
 In 2014, Worley Parsons created a supply chain simulation of a complex logging operation in New Zealand focusing on port operations to assist in assessing throughput improvement options. This project undertook significant historical data modelling to create a robust, stochastic truck and docket arrivals generator that feeds a detailed port-side storage and log handling simulation. The simulation enables future annual target throughput to be defined, and from this a realistic logging and shipping operation is simulated. It enables detailed quantitative assessment of the likely impacts of alternate business improvement options. Primary skills applied were:
In 2014, Worley Parsons created a supply chain simulation of a complex logging operation in New Zealand focusing on port operations to assist in assessing throughput improvement options. This project undertook significant historical data modelling to create a robust, stochastic truck and docket arrivals generator that feeds a detailed port-side storage and log handling simulation. The simulation enables future annual target throughput to be defined, and from this a realistic logging and shipping operation is simulated. It enables detailed quantitative assessment of the likely impacts of alternate business improvement options. Primary skills applied were:
- Data cleansing, interpretation and modelling to fit input data probability densities (continuous and empirical).
- Use of ExtendSim's advanced resource management capability in a pseudo-object oriented model architecture.
- Monte Carlo sampling in a discrete event simulation with statistical results analysis.
 An ExtendSim consultant working for the Queensland Fire Service, built a custom block and model in ExtendSim to interface with an advanced wildfire simulator called Phoenix RapidFire - a deterministic wildfire spread simulation used across Australia's emergency services. Being deterministic, a recognized operational problem is that Phoenix only gives a single best guess spread prediction for a given set of inputs. By using ExtendSim to pull in the original Phoenix project and fuel types as .xml files, the consultant could define the levels of certainty for the forecast weather stream, the point and time of ignition, and the fuel loads inputs so the ExtendSim model could generate a stochastic version of the Phoenix files. The result is a bunch of shape files (possible fire spread futures) that a GIS team uses to create a single probabilistic fire spread map and a bunch of other really powerful spin off products. These are used during the fire season in the field to help better manage wildfire response and enhance community safety.
An ExtendSim consultant working for the Queensland Fire Service, built a custom block and model in ExtendSim to interface with an advanced wildfire simulator called Phoenix RapidFire - a deterministic wildfire spread simulation used across Australia's emergency services. Being deterministic, a recognized operational problem is that Phoenix only gives a single best guess spread prediction for a given set of inputs. By using ExtendSim to pull in the original Phoenix project and fuel types as .xml files, the consultant could define the levels of certainty for the forecast weather stream, the point and time of ignition, and the fuel loads inputs so the ExtendSim model could generate a stochastic version of the Phoenix files. The result is a bunch of shape files (possible fire spread futures) that a GIS team uses to create a single probabilistic fire spread map and a bunch of other really powerful spin off products. These are used during the fire season in the field to help better manage wildfire response and enhance community safety. RSG's Public Lands Planning and Management group model visitor use at national parks and forests, providing a basis for standards that frame acceptable conditions. The goal is to optimize park operations and maximize visitor experiences while minimizing search-and-rescue incidents in the wilderness areas such as the Half Dome Trail.
RSG's Public Lands Planning and Management group model visitor use at national parks and forests, providing a basis for standards that frame acceptable conditions. The goal is to optimize park operations and maximize visitor experiences while minimizing search-and-rescue incidents in the wilderness areas such as the Half Dome Trail. In collaboration with a major utility facing major storms on an annual basis, Davies Consulting Inc. developed an innovative simulation model using ExtendSim that allowed decision makers to evaluate the affect of strategic decisions on storm restoration prior to and after a storm has struck.
In collaboration with a major utility facing major storms on an annual basis, Davies Consulting Inc. developed an innovative simulation model using ExtendSim that allowed decision makers to evaluate the affect of strategic decisions on storm restoration prior to and after a storm has struck.
Case Studies
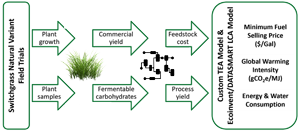
Economic and Sustainability Impacts of Yield and Composition Variation in Bioenergy Crops: Switchgrass
Renee M. Happs, Rebecca J. Hanes, Andrew W. Bartling, John L. Field, Anne E. Harman-Ware, Robin J. Clark, Thomas H. Pendergast IV, Katrien M. Devos, Erin G. Webb, Ali Missaoui, Yaping Xu, Shiva Makaju, Vivek Shrestha, Mitra Mazarei, Charles Neal Stewart Jr., Reginald J. Millwood, Brian H. Davison
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, Volume 12, Issue 5
January 22, 2024
Economically viable production of biobased products and fuels requires high-yielding, high-quality, sustainable process-advantaged crops, developed using bioengineering or advanced breeding approaches. Understanding which crop phenotypic traits have the largest impact on biofuel economics and sustainability outcomes is important for the targeted feedstock crop development. Here, we evaluated biomass yield and cell-wall composition traits across a large natural variant population of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) grown across three common garden sites. Samples from 331 switchgrass genotypes were collected and analyzed for carbohydrate and lignin components. Considering plant survival and biomass after multiple years of growth, we found that 84 of the genotypes analyzed may be suited for commercial production in the southeastern U.S. These genotypes show a range of growth and compositional traits across the population that are apparently independent of each other. We used these data to conduct techno-economic analyses and life cycle assessments evaluating the performance of each switchgrass genotype under a standard cellulosic ethanol process model with pretreatment, added enzymes, and fermentation. We find that switchgrass yield per area is the largest economic driver of the minimum fuel selling price (MSFP), ethanol yield per hectare, global warming potential (GWP), and cumulative energy demand (CED). At any yield, the carbohydrate content is significant but of secondary importance. Water use follows similar trends but has more variability due to an increased dependence on the biorefinery model. Analyses presented here highlight the primary importance of plant yield and the secondary importance of carbohydrate content when selecting a feedstock that is both economical and sustainable.
Rob Brownie
Insight Acumen
2023
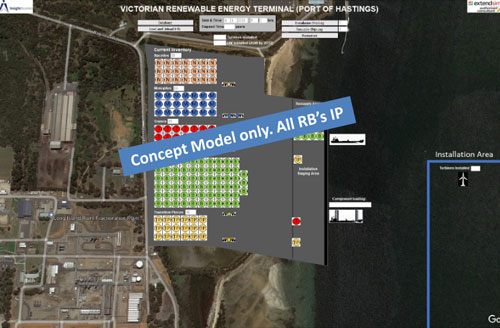
Offshore wind is important to Victoria's move to renewable energy. The Victorian Government has set ambitious targets of 2 GW by 2032, 4 GW by 2035 and 9 GW by 2040.
Using ExtendSim discrete event simulation software we built a representation of the proposed Port of Hastings terminal in operation for offshore wind installation, using 100% open source information and best "guesstimates".
Model was built with sufficient detail to answer "what if" type questions and to undertake sensitivity analysis.
For more customer and concept models, or more on Insight Acumen, visit www.insightacumen.com.au.
Development of the IBSAL-SimMOpt Method for the Optimization of Quality in a Corn Stover Supply Chain
Hernan Chavez & Krystel K. Castillo-Villar from the Mechanical Engineering Department at The University of Texas at San Antonio and Erin Web from the Environmental Sciences Division at Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Energies, Volume 10, Issue 8
August 2017
Up until now, most of the models developed to optimize biomass supply chains have failed to quantify the effect of biomass quality and the preprocessing operations required to meet biomass specifications on overall cost and performance. However, the IBSAL-SimMOpt method provides a novel approach for finding near-optimal solutions to the problem of designing biomass supply chains that improve the physical characteristics of the feedstock at an acceptable cost. The bioenergy sector and the research community now have access to a simulation-based optimization model with activity-based costing that is capable of representing the stochastic behavior of some elements intervening in the corn stover supply chain for the production of bioethanol. This analytical model can be used for decision making as well as educational and training purposes since it allows the user to conduct “what if” scenarios.
A Prototype Simulation-based Optimization Approach to Model Feedstock Development for Chemical Process Industry
Ismail Fahmi, University of Tulsa
12AIChE Conference • Pittsburgh, PA • November 1, 2012
Chemical Engineering Research and Design • Special Issue: Computer Aided Process Engineering (CAPE) Tools for a Sustainable World • Volume 91, Issue 8 •August 2013
Incorporating non-traditional feedstocks, e.g., biomass, to chemical process industry (CPI) requires investments in research & development (R&D) and capacity expansions. The impact of these investments on the evolution of biomass to commodity chemicals (BTCC) system should be studied to ensure a cost-effective transition with acceptable risk levels. The BTCC system includes both exogenous, e.g., product demands (decision-independent) and endogenous, e.g., the change in technology cost with investment levels (decision-dependent) uncertainties. This report presents a prototype simulation-based optimization (SIMOPT) approach to study the BTCC system evolution under exogenous and endogenous uncertainties, and provides a preliminary analysis of the impact of using three different sampling methods, i.e., Monte Carlo, Latin Hypercube, and Halton sequence, to generate the simulation runs on the computational cost of the SIMOPT approach. The results of a simplified case study suggest that annual demand increases is the dominant factor for the total cost of the BTCC system. The results also suggest that using Halton sequence as the sampling method yields the smallest number of samples, i.e., the least computational cost, to achieve a statistically significant solution
Project presented at
 12AIChE Conference
12AIChE Conference
Pittsburgh, PA
November 1, 2012
![]() oral presentation
oral presentation
![]() poster presentation
poster presentation
Project published in
 Chemical Engineering Research and Design
Chemical Engineering Research and Design
Special Issue: Computer Aided Process Engineering (CAPE) Tools for a Sustainable World
Volume 91, Issue 8 •August 2013
Interstate Commission on the Potomac River Basin
Joseph Hoffman, Gregory J. Prelewicz, P.E. Erik R. Hagen, and P.E. Ani Kame’enui
Section for Cooperative Water Supply Operations on the Potomac
June 2011
The Potomac Reservoir and River Simulation Model (PRRISM) was originally developed using Fortran by a research team at Johns Hopkins University in 1982. In the late 1990’s, the CO-OP section of the Interstate Commission on the Potomac River Basin (ICPRB) converted the model to an ExtendSim model. PRRISM simulates the physical processes and operations of four reservoirs and the allocation of water within the Washington Metropolitan Area (WMA) at daily time scale. It determines the amount of water available to each of the several jurisdictions, for given streamflows, demands, and weather allocation and reservoir operation rules. When operating in batch mode, PRRISM performs the functions of a regional water supply manager in strict accordance with rules specified by the model user. This interactive model allows participants to engage in a dialogue with the model as it is being executed, changing model parameters and overriding prespecified decision rules. Today PRRISM is a deterministic continuous simulation model that is regularly updated to reflect system changes. This model continues to serve as a long-term planning tool with which water supply management decisions are made.

Blue Plan-It® Decision Support System
Blue Plan-it takes an agency’s vast quantity of data, including maintenance, geographic, regulatory, and financial information, and creates a customized graphical user interface that can be easily modified, understood, and presented.
Developed by Carollo to help their clients manage complex, interconnected water and wastewater infrastructure, storage, treatment, conveyance, and distribution systems, Blue Plan-it is a fully customizable simulation and optimization model suite developed in ExtendSim. Featured with a simple but powerful “Drag and drop” interface, Blue Plan-it allows for rapid model configuration by dragging blocks from premade libraries into a model window, connecting the blocks, and then setting or adjusting the preset dialog parameters. BLUE PLAN-IT®
ONE WATER SUITE
M.Lample, D.Bailly, J.Ballé-Béganton
International Environmental Modelling and Software Society (iEMSs)
2012 International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software
The quantitative water management of the Charente River in France is a major policy concern because of freshwater scarcity in summer. In the context of the SPICOSA project (Science and Policy Integration for Coastal System Assessment) as mentioned below, this policy issue was chosen to apply the System Approach Framework (SAF) methodology. This led to modeling irrigation management strategies to quantify its impacts on various uses.
They built an external hydrological model in HEC-HMS (Hydrologic Engineering Center's Hydrologic Modeling System) and interfaced with ExtendSim to work as a source of forcing. This strategy proved to be more efficient to model water shortages without renouncing the benefits of system-modeling inside the ExtendSim platform and with the advantage of a software dedicated to hydrological modeling. Using this experiment, the paper discusses the case of “in-line”, “on-line”, or “off-line” coupling modes to serve the objectives of policy orientated complex socio-ecosystems modeling.
DOE Bioenergy Technology Office Feedstock Platform Review
Shahab Sokhansanj, Erin Webb, Anthony Turhollow
ORNL Environmental Sciences Division
May 2013
This project contains a wealth of biomass feedstock information resources from the U.S. Department of Energy, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Idaho National Laboratory, National Renewable Energy Laboratory, and other research organizations
This consortium used ExtendSim to create the Integrated Biomass Supply Analysis & Logistics (IBSAL) model. This biomass supply chain model starts from defining the logistical features of the supply such as number of farms involved, average yield, the start and progress of harvest schedule, and the moisture content of the crop.
The model also requires daily weather data such as temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, rainfall and snow fall. A spreadsheet containing equipment specifications provides data for calculating service times. This information is used in calculating drying and wetting of the biomass and workability of the soil. The user also defines the safe moisture content for baling and minimum temperature below which farm operations will cease. Once all input parameters are identified, the model calculates costs per ton of biomass, energy input and emissions (CO2) from equipment.


Using GIS and Intelligent Transportation Tools for Biomass Supply Chain Modeling and Cost Assessment
Slobodan Gutesa
Thesis submitted to the graduate faculty in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Agricultural Engineering at Iowa State University
2013
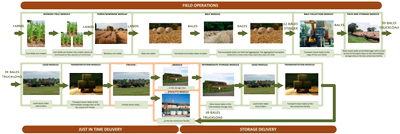
Stable, functional, and efficient bioethanol production systems on the national level must emphasize solutions of feedstock availability and transportation problems. Transportation logistics are a critical factor in the optimization of biomass supply chains. A single 25 million gallon per year cellulosic ethanol biorefinery will require delivery of 18,500 semi loads of bales to the plant. For a typical corn-stover biomass supply chain, baled corn stover must be transported in two phases, first from the field to a storage site and then from the storage site to the biorefinery. All activities between these two points are interconnected and together they form the biomass supply chain. The goal of supply-chain optimization is to minimize the total cost of these activities (transportation cost per unit, inventory cost per unit etc.) while satisfying the supply demands of a biorefinery.
A model of the supply-chain representing a realistic biomass transportation cycle between a single cornfield and biomass storage was created in ExtendSim. It included multiple simulations using different model factors providing a complete assessment of influence of various factors on system productivity.

Simulating Global Warming
Fairchild Tropical Botanical Garden
A comprehensive middle school and high school environmental education program coupled with support from the National Science Foundation created an ExtendSim model simulating the effects of rainforest deforestation and agriculture (planting pasture crops) on the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere and on animals living in the rainforest. Hence, the Rainforest Carbon Cycling Model was born.
The Rainforest Carbon Cycling Model makes a tropical rain forest come alive as carbon from the air flows through it! Designed for users with no previous modeling experience, this model allows users to delve into ‘What if?’ sorts of questions about factors that limit forest production and the effects of land-use change on carbon cycling and global warming.
Rainforest Carbon Cycling Model History
Ann Russell, Terrestrial Ecosystems Ecologist at Iowa State University had a dream to develop a model of carbon cycling in a tropical rain forest using ExtendSim energy language model. Using data collected from research in a Costa Rican rainforest, Jim Dailey of Jim Dailey & Associates transformed the data into an animated, bilingual model for children and the general public and called it the Rainforest Carbon Cycling Model.
The model was distributed to 45,000 children in the Miami-Dade County school system through an outreach program organized by the Fairchild Tropical Botanical Gardens in Coral Gables, Florida called the Fairchild Challenge
Fairfield Challenge Overview
Designed for students of diverse interests, abilities, talents and backgrounds, the Fairchild Challenge is Fairchild Tropical Botanic Garden's environmental education outreach program. With separate but parallel programs for different grade levels 6 to 8 and 9 to 12, the Fairchild Challenge is composed of multidisciplinary competitions aligned with Sunshine State Standards.
The annual Fairchild Challenge options are intended to appeal to students' sense of play and creativity, to encourage them to experiment with ideas, projects and skills and to empower them to seek information and voice opinions. This free program was originally open to all schools in the greater Miami area. As of January 2010, 92 middle schools and 61 high schools are actively participating in the Fairfield Challenge. Other sites are replicating the Fairchild Challenge model nationally and abroad.
A Study on Carriage Road Use in Acadia National Park, Maine, USA
Benjamin Wang and Robert E. Manning
Environmental Management
January 1999
Simulation is used as a tool for describing visitor travel on the carriage roads of Acadia National Park, Maine, USA. The findings of this study suggest that computer simulation is useful for estimating current carrying capacity conditions, predicting future conditions, and guiding related research.
Edwin P. Maurer, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Santa Clara University, Santa Clara, CA & Dennis P. Lettenmaier, Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, WA
Journal of Climate - Issue 17, Volume 2
2004
Using ExtendSim, the authors constructed a system model, MOSIM, that uses the physical reservoir data and minimum releases for hydropower and environmental constraints from a long-term study of the Missouri River basin. The value was based on the hydropower generated by the main-stem dams for a simulated period of 1898–1996 using MOSIM. Simulated forecasted flows were generated to represent the levels of predictability that had been determined in a previous study. The results demonstrate that use of climate forecast information along with better definition of the basin moisture states can improve runoff predictions with modest economic value that, in general, will increase as the size of the reservoir system decreases.
Science and Policy Integration for Coastal Assessment
A four-year project that was funded by the European Union’s 6th Framework Programme for Research
2007 to 2011
54 partner institutes in 21 countries used ExtendSim to study 18 coastal sites in the EU project SPICOSA. This project assisted Europe in its goal of achieving Sustainable Development by developing and testing a conceptual methodological framework for transition in coastal zones. The SPICOSA initiative originates from the fact that coastal systems are under increasing human pressure and policy had not been able to respond properly to the resulting negative impacts on ecological, social and economic systems.
SPICOSA´s overall aim was to develop a self-evolving, holistic research approach and support tools for the assessment of policy options for sustainable management through a balanced consideration of the ecological, social and economic aspects of Coastal Zone Systems (Integrated Coastal Zone Management).
All 18 study sites of SPICOSA used ExtendSim to describe a variety of coastal processes ranging from eutrophication, fisheries, and beach attractiveness to clam culture. They created a generic model library containing a complete set of reusable model components which were used to (re)build coastal models for new study areas, not much unlike the well-known Lego bricks.
The population of such a model library was one of the key challenges of the project and served several purposes:
- Existing models are easier to expand or maintain.
- New models were easier to build.
- Quick exchange of models within the scientific community.
- Avoidance of unnecessary modelling (not “reinventing the wheel”).
The principles of generic modelling were elaborated upon during the SPICOSA Cluster Workshops. For more information about ExtendSim use and its history in SPICOSA projects, read the series of newsletters on the SPICOSA site.

Low Impact Feasibility Evaluation (LIFE™) Model
Interactive Tool For Designing Low Impact Developments
Robert Larsson, Lund University
Daniel E. Medina, Patrick Graham, Jared Thorpe, Avinash Patwardhan, Timothy Hare
Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, National TMDL Science and Policy
2003
Developed in ExtendSim, the LIFE (Low Impact Feasibility Evaluation) model established functional connections between different land uses and landscape features. It has been used for:
- Design of volume or water quality based stormwater controls.
- Review of development/re-development plans for compliance with stormwater regulations.
- Incentive-based approaches such as environmental credit trading.
- Public education and outreach.






 Watch Video
Watch Video


 Download Climate Change & Washington Metropolitan Area Water Supply Report
Download Climate Change & Washington Metropolitan Area Water Supply Report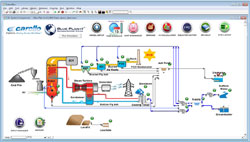
 Go to A Passion for Water article about Blue Plan-It
Go to A Passion for Water article about Blue Plan-It