 The ExtendSim Academic Research Grant program has helped many, many students over the years achieve their dreams. At the same time, it has supported essential phases of innovative research projects in universities worldwide.
The ExtendSim Academic Research Grant program has helped many, many students over the years achieve their dreams. At the same time, it has supported essential phases of innovative research projects in universities worldwide.
Here's just a few projects that have utilized ExtendSim as part of the Academic Research Grant program and helped students with their advanced degrees.
see Academic Research Grants in Progress![]()
apply for an Academic Research Grant ![]()
update form for current Academic Research Grant holders ![]()
Completed Academic Research Grants
Biofuel Supply Chain
 Simulation-Based Approach for the Optimization of a Biofuel Supply Chain
Simulation-Based Approach for the Optimization of a Biofuel Supply Chain
Hernan Chavez Paura Garcia
University of Texas at San Antonio
PhD in Supply Chain Optimization • February 23, 2017
Project presented at
 The 2017 IISE Annual Conference.
The 2017 IISE Annual Conference.
Abstract
The billion-ton study lead by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory indicates that the U.S. can sustainably produce over a billion ton of biomass, annually. However, the delivery of the biomass required to meet the required goals is particularly challenging. This is mainly because of the physical properties of biomass. This research work focuses on the use of agricultural residues to produce second-generation biofuels. Second generation biomass exhibits more quality variability (e.g., higher ash and moisture contents) than first generation. The purpose of this study is to quantify the cost of imperfect feedstock quality in a biomass-to-biorefinery supply chain (SC) and to develop a discrete event simulation coupled with an optimization algorithm for designing a biofuel SC's. This work presents a novel optimization approach based on an extended Integrated Biomass Supply and Logistics (IBSAL) simulation model for estimating the collection, storage, and transportation costs. The presented extension of the IBSAL considers the cost incurred for having imperfect feedstock quality and finds the optimal SC design. The applicability of this methodology is illustrated by using a case study in Ontario, Canada. A converging set of non-dominated solutions is obtained from computational experiments. Sensitivity analysis is performed to evaluate the impact of different scenarios on overall costs. Preliminary results are presented.
IBSAL-SimMOpt Approach
The approach presented in this work is a two-phase model that uses an extension of the IBSAL model in the initial phase, and searches a near-optimal set of solutions in the second phase by using an optimization procedure based on the SimMOpt model. The IBSAL model is a time-dependent discrete event simulation (DES) model with activity-based costing. The model in the proposed approach estimates the cost of imperfect feedstock quality and evaluates its effect on the performance of the SC.
The SimMOpt model is a simulation-based multi-objective optimization approach based on stochastic Simulated Annealing (SA).
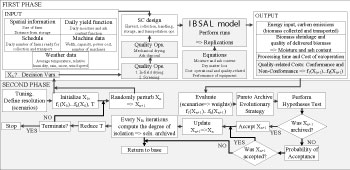
The solutions for near-optimal quality-related costs are found by using the extension of the IBSAL implemented in ExtendSim and the SimMOpt-based procedure included in written in MS VBA®™ language. This figure is a diagram of the proposed approach.
Case Study
The characteristics of the system described in this research include a geographical implementation (i.e., Southern and Western Ontario, Canada), crop availability (ac), corn yield (bu/ac), sustainable production (dry tonne/ac), among others. The geographical implementation corresponds to 20 farms located in the following counties: Lambton, Chatam-Kent, Middlesex, and Huron.
The initial moisture content is modeled by ~U(0.6, 0.8). The moisture content after the natural drying process is assumed to follow ~U(0.15, 0.3). The moisture content requirement for thermochemical processes is 20%. If the content remains above 20%, the stover goes through a mechanical drying process. The cost of the natural air drying system is given by (0.014 * (Initial Moisture Content – Final Moisture Content) * 100) + 0.05 per bushel and the in-bin, stirred system is given by (0.033 * (Initial Moisture Content) * 100) + 0.048 per bushel. Similarly, the initial ash content follows ~U(0.08,0.12). The ash content after the screening process is assumed to follow ~U(0.1, Initial Ash Content). The screening cost is given by 135(Initial Ash Content – Final Ash Content) per dry tonne. The cost of disposing ash is given by 28.86(Final Ash Content) per dry tonne. The binary decision variables in this model represent the decisions of performing the field drying and the screening activities at each farm.
Results and Conclusions
The SA was tuned through designed computational experiments. The SA schedules have a relevant effect on the set of these preliminary solutions. Figure 3 shows the Pareto front including four schedules. The non-dominated solution that balances out the conformance and nonconformance costs (i.e., (0.4/0.6) and (0.6/0.4) weights) shows a conformance cost (the cost incurred to prevent biomass poor quality) of $49,899.47 and a non-conformance cost (cost incurred to fixed biomass poor quality) of $16,496.83 for all 20 farms. This non-dominated solution was found when using the schedule that computes the largest number of initial solutions (i.e., Schedule 4 → 50 initial solutions). This preliminary results highlighted the trade-off between conformance and conformance activities implemented into a biofuel SC. The impact of quality-related activities in the SC topology, design and planning decisions will be studied next.
Acknowledgements
This material is based upon work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, Bioenergy Technologies Office (4000142556) and U.S. Department of Agriculture/National Institute of Food and Agriculture (2015-38422-24064). The fellowship from the Mexican Council for Science and Technology (CONACYT) is gratefully acknowledged. The support provided by Imagine That!®™ by donating of a full version of ExtendSim®™ through the ExtendSim Research Grant is gratefully acknowledged. The research work on the IBSAL model by Sokhansanj, Turhollow, Ebadian and Webb was relevant for the development of the proposed approach.
Previous Publications and Refereed Conference Proceedings
Aboytes, M., Chavez, H., Krishnaiyer, K., Stankus, S. & Taherkhorsandi, M. "Improving Radio Frequency Identification Accuracy in a Warehouse Setting". Abstract accepted in the 2016 Engineering Lean & Six Sigma Conference, San Antonio, TX, September 14 - 16, 2016.
Chávez, H. & Castillo-Villar, K. K. "Stochastic Multi-Objective Simulated Annealing for the Optimization of Machining Parameters". Abstract accepted in the 2016 Industrial and Systems Engineering Research Conference (ISERC), Anaheim, California, May 21 - 24, 2016.
2016 ISERC Best Track Paper: Manufacturing and Engineering Design.
Chávez, H., Castillo-Villar, K. K., Herrera, L., & Bustos, A. "Simulation-based multi-objective model for supply chains with disruptions in transportation". Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing.. Ms. Ref. No.: RCIM-D15-00130. 2016.
Stankus, S., Chávez, H., Castillo-Villar, K. K., & Feng, Y. "A Simulation-based Optimization Approach to Modeling a Fast-track Emergency Department". Abstract accepted in the 2015 Industrial and Systems Engineering Research Conference (ISERC), Nashville, Tennessee, May 30 - June 2, 2015.
Chavez, H. & Castillo-Villar K.K. "A Preliminary Simulated Annealing for Resilience Supply Chains". Paper on proceedings of the IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence 2014, Orlando, Florida, USA, December 12, 2014.
Chavez, Hernan, Castillo-Villar, K. K., Herrera, Luis & Bustos, A. "Simulation-based Optimization Model for Supply Chains with Disruptions in Transportation". Paper submitted on the Flexible Automation and Intelligent Manufacturing (FAIM) Conference 2014, San Antonio, TX, May 20-23. 2014.
Scientific Posters
Chavez, H., Webb, E., Castillo-Villar, K.K., Ebadian, M., & Sokhansanj, S. "Modeling Cost of Quality in a Discrete Event Biomass Supply Chain". IBSS (Southern Partnership for Integrated Biomass Supply Systems) Annual Meeting. July 27th, 2016.
Chavez, H., Webb, E., Castillo-Villar, K.K., Ebadian, M., & Sokhansanj, S. "Modeling Cost of Quality in a Discrete Event Biomass Supply Chain". ORISE (Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education) Summer Graduate, Post Graduate, Employee Participant, and Faculty Poster Session. August 9th, 2016.
Technical Reports
Castillo-Villar, K. K., Rogers, Dwain & Chavez, Hernan. "AFV's Fleet Replacement Optimization (Alternative Transportation Initiatives)". (City Public Services (CPS) Energy (San Antonio Water System (SAWS)) & Austin Public Transit (Capital Metro):). Summer 2015. Granting Agency: CPS through Texas Sustainable Energy Research Institute. 2015.
Castillo-Villar, K.K., & Chávez, H. "Simulation-based Optimization Model for Supply Chains with Disruptions in Transportation", Mexico Center Educational Research Fellowship - International Study Fund, 2013-2014, Funded by Mexico Center, UTSA. 2014.
Castillo-Villar, K.K., & Chávez, H. "Reliability Project in Toyota Manufacturing from Reactive to Proactive Maintenance, San Antonio, TX". The University of Texas at San Antonio, Technical Report, June 2014, 68 and 21 pages. Granting Agency: Toyota Motor Manufacturing Texas. 2014.
Biomass to Commodity Chemicals
 Simulation-Based Optimization of Biomass Utilization to Energy and Commodity Chemicals
Simulation-Based Optimization of Biomass Utilization to Energy and Commodity Chemicals
Ismail Fahmi
University of Tulsa
PhD in Chemical Engineering • August 2013
Project presented at
 12AIChE Conference
12AIChE Conference
Pittsburgh, PA
November 1, 2012
 oral presentation
oral presentation
 poster presentation
poster presentation
Project published in
 Chemical Engineering Research and Design
Chemical Engineering Research and Design
Special Issue: Computer Aided Process Engineering (CAPE) Tools for a Sustainable World
Volume 91, Issue 8 •August 2013
Abstract
Incorporating non-traditional feedstocks, e.g., biomass, to chemical process industry (CPI) will require investments in research & development (R&D) and capacity expansions. The impact of these investments on the evolution of biomass to commodity chemicals (BTCC) system should be studied to ensure a cost-effective transition with acceptable risk levels. The BTCC system includes both exogenous, e.g., product demands (decision-independent) and endogenous, e.g., the change in technology cost with investment levels (decision-dependent) uncertainties.
This paper presents a prototype simulation-based optimization (SIMOPT) approach to study the BTCC system evolution under exogenous and endogenous uncertainties, and provides a preliminary analysis of the impact of using three different sampling methods, i.e., Monte Carlo, Latin Hypercube, and Halton sequence, to generate the simulation runs on the computational cost of the SIMOPT approach. We realized that the simulation-based optimization framework that we developed has two major computational costs:
- The cost associated with the required number of samples to obtain the model with sufficient statistical significance.
- The cost associated with solving the optimization problem.
The results of a simplified case study suggest that annual demand increases is the dominant factor for the total cost of the BTCC system. The results also suggest that using Halton sequence as the sampling method yields the smallest number of samples, i.e., the least computational cost, to achieve a statistically significant solution. Other conclusions that we can take from this work are:
- BTCC system evolution is highly dependent on the costs of the raw material.
- Investing in the non-renewable processing technologies is attractive in long term.
- The developed SIMOPT framework can be used to include the endogenous and exogenous uncertainties of the BTCC system evolution.
- The developed optimization module is universal, meaning that it is independent of technology types.
- The developed optimization module can also incorporate the relationships between maturity stage and the ability to incorporate to overall production.
- Halton series is shown to be the most appropriate sampling method.
- Bilinear relaxation with linearly segmented tight relaxation coupled with nonlinear terms relaxation with linear upper and under estimators is shown to be able to obtain a good initialization for the optimization module.
Other Publications by this Researcher
Fahmi, Ismail and Selen Cremaschi. "A Prototype Simulation-based Optimization Approach to Model Feedstock Development for Chemical Industry". Proceedings of the 22nd European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering, 2012.
Fahmi, Ismail and Selen Cremaschi. "Stage-gate Representation of Feedstock Development for Chemical Process Industry". Foundations of Computer-Aided Process Operations, 2012.
Call Centers • Routing Rules
 Knowledge Management in Call Centers: How Routing Rules Influence Expertise in the Presence of On-the-Job Learning
Knowledge Management in Call Centers: How Routing Rules Influence Expertise in the Presence of On-the-Job Learning
Geoffrey Ryder
University of California at Santa Cruz
PhD in Operations Research • March 16, 2011
Abstract
In this paper, the effect that routing rules have on agent learning is researched. A nonlinear optimization framework for two kinds of expertise objectives are developed: one that seeks equal distribution of experience across the workforce (effectively cross-training) and one that aims to develop specialized expertise by prioritizing the routing of specific customer inquiries to specific agents. Analytical models of call center operations are inadequate to handle this task, so instead we turn to discrete-event simulation, and evaluate the effect of routing policies on agent expertise with a custom simulator developed in the ExtendSim modeling environment. Simulation results describe an efficient frontier in routing policies that depends on the underlying expertise objective function.
Other Publications by this Researcher
Ryder, G. "Managing Changing Service Capacity Based on Agent Performance Data". INFORMS Annual Meeting, Service Industry III Session, Nov. 7, 2007.
Ryder, G. "How Learning and Forgetting Affect the Optimal Work Policy." INFORMS Annual Meeting, Management of Complex Service Systems Session, Nov. 4, 2007.
Ryder, G. and Ross, K. "Optimal Service Rules in the Presence of Learning and Forgetting". Sixteenth Annual Frontiers in Service Conference, San Francisco. October 4, 2007.
Ryder, G., Ross, K., and Musacchio, J. "Optimal service policies under learning effects". International Journal of Services and Operations Management, Issue 6, Vol. 4, 2008.
Ryder, G. and Ross, K. "Optimal service policies in the presence of learning and forgetting". Applied Probability Track, INFORMS Annual Conference, Pittsburg, PA, 2006.
Ryder, G. "A probability collectives approach to weighted clustering algorithms for ad hoc networks". IASTED CCN Conference, Marina Del Rey, CA, October 2005.
Chemical • Processing Multi-Products
 An Efficient Method for Optimal Design of Large-Scale Integrated Chemical Production Sites with Endogenous Uncertainty
An Efficient Method for Optimal Design of Large-Scale Integrated Chemical Production Sites with Endogenous Uncertainty
Sebastian Terrazas-Morenoa, Ignacio E. Grossmanna, John M. Wassick, Scott J. Bury, Naoko Akiya
Carnegie Mellon University
PhD in Chemical Engineering • March 2012
Project published in
Computers & Chemical Engineering
Volume 37 • February 2012
Abstract
Integrated sites are tightly interconnected networks of large-scale chemical processes. Given the large-scale network structure of these sites, disruptions in any of its nodes, or individual chemical processes, can propagate and disrupt the operation of the whole network. Random process failures that reduce or shut down production capacity are among the most common disruptions. The impact of such disruptive events can be mitigated by adding parallel units and/or intermediate storage. In this paper, the design of large-scale, integrated sites considering random process failures in addressed. In a previous work (Terrazas-Moreno et al., 2010), a novel mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) model was proposed to maximize the average production capacity of an integrated site while minimizing the required capital investment. The present work deals with the solution of large-scale problem instances for which a strategy is proposed that consists of two elements. On one hand, we use Benders decomposition to overcome the combinatorial complexity of the MILP model. On the other hand, we exploit discrete-rate simulation tools to obtain a relevant reduced sample of failure scenarios or states. We first illustrate this strategy in a small example. Next, we address an industrial case study where we use a detailed simulation model to assess the quality of the design obtained from the MILP model.
"A Mixed-Integer Linear Programming Model for Optimizing the Scheduling and Assignment of Tank Farm operations"
Sebastian Terrazas-Morenoa, Ignacio E. Grossmanna, John M. Wassick
Carnegie Mellon University
Abstract
This paper presents a novel mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) formulation for the Tank Farm Operation Problem (TFOP), which involves simultaneous scheduling of continuous multi-product processing lines and the assignment of dedicated storage tanks to finished products. The objective of the problem is to minimize blocking of the finished lines by obtaining an optimal schedule and an optimal allocation of storage resources. The novelty of this work is the integration of a tank assignment problem with a scheduling problem where a dedicated storage tank has to be chosen from a tank farm given the volumes, sequencing, and timing of production of a series of products. The scheduling part of the model is based on the Multi-operation Sequencing (MOS) model by Mouret et al., (2011). The formulation is tested in three examples of different size and complexity.
Closed Loop Supply Chains • Metamodeling of Deteriorating Reusable Articles
 Metamodeling of Deteriorating Reusable Articles in a Closed Loop Supply Chain
Metamodeling of Deteriorating Reusable Articles in a Closed Loop Supply Chain
Eoin Glennane
Dublin City University
Masters in Renewable Energy • June 2021
Abstract
This paper presents a closed loop supply chain for a reusable, deteriorating tool. The tool is used in a manufacturing process on an item in a linear supply chain. A model is created for the linear item supply chain and the tools closed loop supply chain to analyse the interactions between them and various input parameters so that output responses of the system can be modelled. Three approaches are taken to model the system, a brute force factorial design, a modified version of a Latin hypercube space filling design, and a fast flexible space filling design. It is found that all three methods can describe responses that require only a few inputs well but cannot accurately predict more complex responses without all of the relevant factors. Space filling designs should be used if more factors are needed as they minimise the total amount of simulations needed to produce an accurate model.
Approach
Using ExtendSim, models were developed to replicate a manufacturing process requiring reusable tools of varying quality. The models are modifiable to examine how changing certain parameters in the inventory control side of the model have an impact on the production side of the model to determine optimal inventory control practices.
Results and Conclusions
 All three models developed for this project, Design Expert, RLHC, and FFFD, accurately predict the response with the least amount of input: High Quality Time between Orders. However, the more complex responses of the system are not accurately captured in any of the three models. One of the reasons for this may be the lack of relevant factors analysed by the simulation. Another reason could be that there is too much unaccounted randomness in the system for the models to accurately predict the more complex performance indicators. The use of space filling designs such as RLHC and FFFD perform well with high numbers of factors and should be explored further. The Design Expert model performs well but the number of simulations required increases exponentially with the number of factors present.
All three models developed for this project, Design Expert, RLHC, and FFFD, accurately predict the response with the least amount of input: High Quality Time between Orders. However, the more complex responses of the system are not accurately captured in any of the three models. One of the reasons for this may be the lack of relevant factors analysed by the simulation. Another reason could be that there is too much unaccounted randomness in the system for the models to accurately predict the more complex performance indicators. The use of space filling designs such as RLHC and FFFD perform well with high numbers of factors and should be explored further. The Design Expert model performs well but the number of simulations required increases exponentially with the number of factors present.
Only two types of space filling designs for metamodel creation were explored in this paper, a modified version of the Latin Hypercube and JMPs Fast Flexible Filing Design. Both methods are one-shot, non-sequential designs so sequential methods[12] may be able to create accurate models with even lower numbers of simulations required.
Closed Loop Supply Chains • Pull Type Production Control Strategies
 Performance Analysis and Development of Pull-Type Production Control Strategies for Evolutionary Optimisation of Closed-Loop Supply Chains
Performance Analysis and Development of Pull-Type Production Control Strategies for Evolutionary Optimisation of Closed-Loop Supply Chains
Jonathan Ebner
Dublin City University
PhD in Manufacturing Engineering • January 2018
Abstract
The objective of this thesis is to establish a Closed-Loop Supply Chain (CLSC) design that is analysed through a series of simulation models, aimed at defining the highest performing production control strategy, whilst considering multiple related variables on both the forward and reverse flow of materials in manufacturing environments. Due to its stochastic nature, the reverse logistics side of the CLSC represents an increased source of variance for the inventory management and control strategies as it implies the erratic supply of returned materials, in addition to the very random customer demand, hence with highly variable inputs on both sides of the productive system, intrinsically inherent to this line of research.
 To test the operational performance of several pull-type production control strategies, a simulation-based research method was designed. The strategies experimented were: Hybrid Extended Kanban CONWIP special case (HEKC-II), Hybrid Kanban CONWIP (HKC), Dynamic Allocation Hybrid Extended Kanban CONWIP special case (DNC HEKC-II) and Dynamic Allocation Hybrid Kanban CONWIP (DNC HKC). All were tested in scenarios with high and low processing time variability and with 90% returned products and 40% returns from an open market system, therefore totaling 16 simulation models. Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms were utilised to generate the Pareto-optimum performance frontier with the objective of simultaneously minimising both performance metrics: The overall average work in progress (WIP) and the average backlog queue length (BL) for the entire CLSC. Processes used in the recovery and recycling of end of life manufactured goods were examined. This research method structures leading factors towards improved economic viability and sustainability of technologies required for the effective implementation of inventory control strategies on highly complex closed-loop supply chains with the focus on the performance metrics and optimum utilisation of resources available for the industry.
To test the operational performance of several pull-type production control strategies, a simulation-based research method was designed. The strategies experimented were: Hybrid Extended Kanban CONWIP special case (HEKC-II), Hybrid Kanban CONWIP (HKC), Dynamic Allocation Hybrid Extended Kanban CONWIP special case (DNC HEKC-II) and Dynamic Allocation Hybrid Kanban CONWIP (DNC HKC). All were tested in scenarios with high and low processing time variability and with 90% returned products and 40% returns from an open market system, therefore totaling 16 simulation models. Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms were utilised to generate the Pareto-optimum performance frontier with the objective of simultaneously minimising both performance metrics: The overall average work in progress (WIP) and the average backlog queue length (BL) for the entire CLSC. Processes used in the recovery and recycling of end of life manufactured goods were examined. This research method structures leading factors towards improved economic viability and sustainability of technologies required for the effective implementation of inventory control strategies on highly complex closed-loop supply chains with the focus on the performance metrics and optimum utilisation of resources available for the industry.
The dynamic allocation strategies proved significant performance improvement, shifting the entire Pareto frontier forward with major advances on both metrics. Furthermore, it happened on all scenarios tested. The modified HEKC-II, with an optimisable parameter that enables it to be overwritten in a way that it can match the well-established HKC, also performed as originally intended and had better results than HKC in some cases, especially with the higher variability level. It also provided grounds for the suggested improvements and flexibilisation of the HEKC strategy.
A major contribution of this thesis was the successful implementation of another advanced control methodology, entitled here the Intelligent Self-Designing Production Control Strategy, which provided maximum control performance. It consisted essentially of DNC HEKC-II with the following modifications: I) Extensive increase of dynamically allocated authorisation cards; II) Further anticipation of the time to trigger the change in the number of cards according to the finished goods buffer level, plus an acceleration/deceleration factor of this change; III) The capability of downsizing itself to become similar to HKC in an optimisation process if diverse production system conditions and variability would require. It displayed a very significant shift of the performance frontier.
Approach
ExtendSim models were created to treat sets of data the author gathered from mathematical models output, from statistically filtered data, histograms and statistics provided from peer reviewed articles, business cases and related recent publications. Then, it was compiled in a intelligible fashion to produce visual scenarios where companies or public entities can see the advantages of CLSC over the long run.
Results and Conclusions
The dynamic allocation policies, particularly the Dynamic Hybrid Extended Kanban CONWIP special case (DNC HEKC-II), throughout the research space in consideration, evidenced very superior production control performance overall.
The proposed factors on the modification approach, namely: I) The Master Pool (MP) to decide the quantifiable level of the authorisation cards dynamic change and, II) The additional demand communication (DE) to provide slower production pace during low demand periods and to avoid the distributed demand starvation. Both provided a measurable development on the inventory management and operations efficiency for the tested strategies implemented in a Closed-Loop Supply Chain environment.
Significant performance improvement was achieved through the multi-objective optimisation, which directly correlates to the technological viability of the CLSCs strength to cope with a high degree of variabilities simultaneously derived from the processing times, supply and demand. This contribution also provided grounds for the architecture of the Intelligent Self-Designing production control strategy.
The dynamic allocation strategies with results had very tight constraints with regards to the allowable range of PACs available. They had less cards available and they would only have had an equal range of cards after the dynamic change triggered it, so it was even more restricted in order to keep the validity for the comparative analysis against the control group HKC.
Scenarios with 40% recycled supply had less observable improvements because of the dynamic change being operational less often and due to the lower variability of the reverse logistics.
The HEKC-II, modified from the work of Dallery and Liberopoulos [4], had better results than HKC by Bonvik et al. [3] in scenarios with higher variability of supply with 90% returned material. It matched the control group HKC results with a lower variability of supply. It also provided grounds for the suggested improvements and flexibilisation of the HEKC Control Strategy.
Construction • Production Variability
 Work-In-Process Buffer Design Methodology for Scheduling Repetitive Building Projects
Work-In-Process Buffer Design Methodology for Scheduling Repetitive Building Projects
Vicente González, Luis Fernando Alarcón, and Pedro Gazmuri
Pontificia Universidad de Católica de Chile
PhD in Construction • July 2008
Abstract
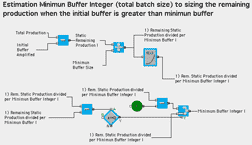 Variability in production is one of the largest factors that negatively impacts construction project performance. A common construction practice to protect production systems from variability is the use of buffers (Bf). Construction practitioners and researchers have proposed buffering approaches for different production situations, but these approaches have faced practical limitations in their application.
Variability in production is one of the largest factors that negatively impacts construction project performance. A common construction practice to protect production systems from variability is the use of buffers (Bf). Construction practitioners and researchers have proposed buffering approaches for different production situations, but these approaches have faced practical limitations in their application.
In Multiobjective Design of Work-In-Process Buffer for Scheduling Repetitive Building Projects, a multiobjective analytic model (MAM) is proposed to develop a graphical solution for the design of Work-In-Process (WIP) Bf in order to overcome these practical limitations to Bf application, being demonstrated through the scheduling of repetitive building projects. Multiobjective analytic modeling is based on Simulation–Optimization (SO) modeling and Pareto Fronts concepts. Simulation–Optimization framework uses Evolutionary Strategies (ES) as the optimization search approach, which allows for the design of optimum WIP Bf sizes by optimizing different project objectives (e.g., project cost, time and productivity). The framework is tested and validated on two repetitive building projects. The SO framework is then generalized through Pareto Front concepts, allowing for the development of the MAM as nomographs for practical use. The application advantages of the MAM are shown through a project scheduling example. Results demonstrate project performance improvements and a more efficient and practical design of WIP Bf. Additionally, production strategies based on WIP Bf and lean production principles in construction are discussed.
Other Publications by this Researcher
González, V., Alarcón, L.F. and Gazmuri, P. "Design of Work In Process Buffers in Repetitive Projects: A Case Study". 14th International Conference for Lean Construction, Santiago, Chile, July 2006.
González, V. and Alarcón, L.F. "Design and Management of WIP Buffers in Repetitive Projects" (White Paper), 2005.
González, V., Rischmoller, L. and Alarcón, L.F. "Management of Buffers in Repetitive Projects: Using Production Management Theory and IT Tools". PhD Summer School, 12th International Conference for Lean Construction, Helsinore, Denmark, August 2004.
González, V., Rischmoller, L. and Alarcón, L.F. "Design of Buffers in Repetitive Projects: Using Production Management Theory and IT Tools". 4th International Postgraduate Research Conference, University of Salford, Manchester, U.K., April 2004.
González, V. and Alarcón, L.F. "Buffer de Programación: Schedule Buffers: A Complementary Strategy to Reduce the Variability in the Processes of Construction", Revista Ingeniería de Construcción Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Volume 18 . Nº 2, pp 109 - 119, Mayo - Agosto 2003.
Cross-Docking • Part I
 CDAP Simulation Report
CDAP Simulation Report
Zongze Chen
University of Pennsylvania
Masters in Electrical & Systems Engineering • May 13, 2010
Abstract
In this project we collaborated with National Retail Systems (NRS) who provided us with realistic cross-dock situations and data to study and to evaluate our modeling and optimization result. The NRS's North Bergen facility receives goods from multiple vendors, sorts and loads them onto outbound trailer trucks for a number of retail stores. Using ExtendSim, I developed a simulation to model of two cross-docks in operation of their New Jersey facility. There were several main objectives to be achieved:
- Develop the model of cross-dock process. For simplicity, we started the development with a 4×4 cross-dock. Later, this would be expanded to realistic dimensions.
- Use the data generated from the GQ3AP algorithm we developed previously to simulate the process and analyze the total cost under the situation and discuss the optimization.
- Improve our optimization models to take into account the impact of truck arrival and departure times. Determine how one can improve cross-docking operations and what costs could be reduced through improved operational control.
The final report describes how simulation helps ensure success of cross-docking systems by determining optimal routing costs. Modeling methods and issues are also discussed as they apply to cross-docking. This report includes discussion of the actual processes employed by NRS, description of our models, simulation results and comparisons, and our conclusions.
Approach
The initial phase of the project involved data collection and acquisition including OD freight volumes and scheduling times. In the next phase in cooperation with NRS, we developed a discrete cross-dock simulation model and found the best optimization methods. Finally, we incorporated what we learned into a set of suggested optimization procedures.
Other Reports by this Researcher
Course Reports in OPIM 910 course (introduction to optimization theory):
Personalized Diet Plans Optimization
University of Pennsylvania Evacuation Plan Design
Classroom Scheduling
Course Reports in STAT 541 course (Statistics Methods):
Boston Real Estate Analysis
Course Reports in STAT 520 course (Applied Econometrics):
Salary Weight Analysis by Gender
Research Assistant on Project at Management Department of Wharton:
Entrepreneurship and Strategy
Cross-Docking • Part II
 Anticipating Labor and Processing Needs of Cross-Dock Operations
Anticipating Labor and Processing Needs of Cross-Dock Operations
Frederick Abiprabowo
University of Pennsylvania
Operations Research • December 2012
Project presented and awarded at
 During the INFORMS Annual Conference 2013, the design team of Frederick Abiprabowo, Napat Harinsuit, Samuel Lim, and Willis Zhang, all from the University of Pennsylvania, were awarded the Undergraduate Operations Research Prize. This competition is held each year to honor a student or group of students who conducted a significant applied project in operations research or management science, and/or original and important theoretical or applied research in operations research or management science, while enrolled as an undergraduate student.
During the INFORMS Annual Conference 2013, the design team of Frederick Abiprabowo, Napat Harinsuit, Samuel Lim, and Willis Zhang, all from the University of Pennsylvania, were awarded the Undergraduate Operations Research Prize. This competition is held each year to honor a student or group of students who conducted a significant applied project in operations research or management science, and/or original and important theoretical or applied research in operations research or management science, while enrolled as an undergraduate student.
Their paper "Designing a Simulation Tool for Commercial Cross-Docking Application" uses ExtendSim to dynamically replicate the operations of a large cross docking facility. The prototype model serves as a tool that enables cross-dock operators to evaluate assignment strategies in a risk-free, costless environment.
Abstract
In the supply chain literature, there are generally three kinds of studies regarding cross-docking:
- Fundamentals of cross-dock
- Distribution planning
- Operations inside the facility
Studies of cross-dock fundamentals take a high-level perspective and discuss the issues of cross-docking in relations to a company’s distribution process, management, etc. Cross-docking can also be viewed as a method in the management of a supply chain. Distribution planning problems pertain to scheduling of trucks, vehicle routing, and network navigation. Finally, there are many research papers regarding the operations inside cross-docks.
Zongze Chen’s CDAP simulation report dealt with the operations inside the cross-docking facility and discussed the formulation of goods movement inside a cross-dock as a GQ3AP. Then, a simulation model was designed after one of the cross-docking facilities of a retail company in New Jersey. This model was then tested to compare the cost of goods movement in two different scenarios
- GQ3AP-optimized door assignment
- Manual door assignment
Based on the results of this test, the scenario with optimized door assignment did yield a lower cost than the one without.
This report continues where the previous report left off and addressed its proposed future plans for the model.
Crowd Management • Modelling Mass Crowd Using Discrete Event Simulation
 A Case Study of Integrated Tawaf and Sayee Rituals during Hajj
A Case Study of Integrated Tawaf and Sayee Rituals during Hajj
Almoaid Abdulrahman A. Owaidah
University of Western Australia
PhD in Philosophy • October 2022
Supervised by: Doina Olaru, Mohammed Bennamoun, Ferdous Sohel, and R. Nazim Khan
Abstract
 Mass Gathering (MG) events bring people together at a specific time and place, which, if not properly managed, could result in crowd incidents (such as injuries), the quick spread of infectious diseases, and other adverse consequences for participants. Hajj is one of the largest MG events, where up to 4 million people can gather at the same location at the same time every year. In the Hajj, pilgrims from all over the world gather in Makkah city in Saudi Arabia for five specific days to perform rituals at different sites.
Mass Gathering (MG) events bring people together at a specific time and place, which, if not properly managed, could result in crowd incidents (such as injuries), the quick spread of infectious diseases, and other adverse consequences for participants. Hajj is one of the largest MG events, where up to 4 million people can gather at the same location at the same time every year. In the Hajj, pilgrims from all over the world gather in Makkah city in Saudi Arabia for five specific days to perform rituals at different sites.
The facilities at the ritual places can become congested and occasionally overcrowded when there are a lot of pilgrims. Overcrowding at Hajj events makes crowd control and management difficult, resulting in many accidents, casualties, and traffic jams. This thesis investigates new simulation and modelling-based crowd management strategies in order to overcome the overcrowding problem at pilgrimage sites and ensure safe and efficient transport of pilgrims. ExtendSim is used to test and validate all simulation models on real Hajj data from previous years, in normal and emergency situations, at different ritual sites, and the impact of arrival scheduling and pilgrim movement between the holy sites. Hajj is a mass gathering event that takes place annually in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Typically, around three million people participate in the event and perform rituals that involve their movements within strict space and time restrictions. Despite efforts by the Hajj organisers, such massive crowd gathering and movement cause overcrowding related problems at the Hajj sites. Several previous simulation studies on Hajj focused on the rituals individually. Tawaf, followed by Sayee, are two important rituals that are performed by all the pilgrims at the same venue on the same day. These events have a strong potential for crowd buildup and related problems. As opposed the previous works in the literature, in this paper we study these two events jointly, rather than separately integrating the Tawaf and Sayee rituals into one model. The validated model was applied to a wide range of scenarios where different percentages of pilgrims were allocated to the various Tawaf and Sayee areas. The effect of such allocations on the time to complete Tawaf and Sayee indicate strategies for managing these two key Hajj rituals.
Approach
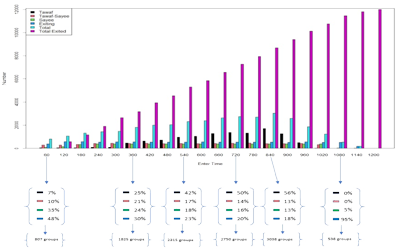 Total number of groups of pilgrims at areas of Tawaf, Sayee, in transit between Tawaf-Sayee and the cumulative number of groups that had exited the GM, over time.Most of the work undertaken before examined in great detail interaction between pilgrims during Tawaf (at the Grand Mosque) and Stoning the Devil (at the Aljamarat Bridge), which represent the most crowded events of the Hajj. Given the confined space and weather conditions, often incidents occur, with tragic consequences. Instead of using an agent-based model to simulate interactions between individuals, I opted for modelling the whole sequence of Hajj at the level of a guided group (up to 250 individuals with a local guide trained specifically for the event). The innovation is in integrating the events and incorporating travel between sites, which has not been undertaken before.
Total number of groups of pilgrims at areas of Tawaf, Sayee, in transit between Tawaf-Sayee and the cumulative number of groups that had exited the GM, over time.Most of the work undertaken before examined in great detail interaction between pilgrims during Tawaf (at the Grand Mosque) and Stoning the Devil (at the Aljamarat Bridge), which represent the most crowded events of the Hajj. Given the confined space and weather conditions, often incidents occur, with tragic consequences. Instead of using an agent-based model to simulate interactions between individuals, I opted for modelling the whole sequence of Hajj at the level of a guided group (up to 250 individuals with a local guide trained specifically for the event). The innovation is in integrating the events and incorporating travel between sites, which has not been undertaken before.
The research will have implications for both academia and practice: understanding the most challenging aspects of Hajj and whether/how scheduling the arrivals of the pilgrims at various sites may alleviate crowding and improve the operation of the whole event provides insights on organising other mass gathering events. It is expected that transport may play a key role in improving the flow, but this has not been tested. On the managerial side, higher performance indicators mean a better experience for the pilgrims, ensuring safe events and without incidents. The results may assist planning of future events, understanding capacity limitations, providing training tips for the local guides on aspects that may cause issues during the event.
Results and Conclusions
Hajj is the largest mass gathering event in the world. Mitigation of overcrowding at Hajj sites is one of the daunting tasks faced by Hajj officials. Prior planning to organise the movements of the pilgrims, especially for the Tawaf and Sayee rituals, is not only recommended for better use of resources, but also to avoid deleterious effects of emergency situations. While previous studies presented different approaches of Tawaf or Sayee management separately, an important contribution of this work is an integrated Tawaf and Sayee model with various scenarios, using ExtendSim as a research method. Various scenarios were developed to offer different managerial options. The scenarios considered different aspects in pilgrim management at entrances and exits of the Grand Mosque, and Tawaf and Sayee rituals.
Without a micro-level description of physical structures and of individual entities or pilgrims, this study offers insights into the optimal allocations of pilgrims to control crowd density in the GM, in the most strained areas in terms of capacity, and on the conditions of evacuation (LoS, flow capacities, times to traverse or cross the GM towards exit gates). In addition, it shows that by scheduling the two rituals and an adequate allocation to the various levels of the Grand Mosque, there is potential for accommodating larger numbers of pilgrims within the same time window of 30 hours. For example, the average duration required for a number of four million pilgrims to complete both Tawaf and Sayee is 1,783 min (assuming current conditions and no critical incidents), which suggests reserves of capacity could be created through planning. Although our target was to simulate 3 million pilgrims, using the same conditions, the model could simulate up to 4 million pilgrims within the allotted 30 hours.
The simulation results confirm that the most critically high crowd density areas (yet preferred by pilgrims) are the Tawaf area (Mataf) and Sayee Ground Level (GL). As indicated, when these areas accommodated 30% to 80% of pilgrims, all pilgrims completed the rituals in a timely fashion. On the contrary, when other Tawaf and Sayee areas were assigned high percentages of pilgrims, the scenarios showed delays and inability to accommodate all pilgrim groups to complete the rituals within 30 hours. Therefore, it is recommended to distribute the pilgrims gradually, starting from the Tawaf and Sayee critical areas (Tawaf area and Sayee GL) followed by other levels. Another managerial method that could be considered in the organisation of the event is the allocation of each pilgrim group to a certain gate for entry and exit.
 download screenshots of ExtendSim model
download screenshots of ExtendSim model
Research site
Almoaid A. Owaidah on Google Scholar.
Other Publications by this Research
A. Owaidah, D. Olaru, M. Bennamoun, F. Sohel and R. Nazim Khan, "Modelling Mass Crowd Using Discrete Event Simulation: A Case Study of Integrated Tawaf and Sayee Rituals during Hajj", in IEEE Access, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3083265.
Digital Twin • Reliability of an Assembly Plant
 Application of Discrete Event Simulation for Assembly Process Optimization • Buffer and Takt Time Management
Application of Discrete Event Simulation for Assembly Process Optimization • Buffer and Takt Time Management
Pontus Persson & Tim Snell
Luleå Tekniska Universitet
Masters in Mechanical Engineering • May 2020
Abstract
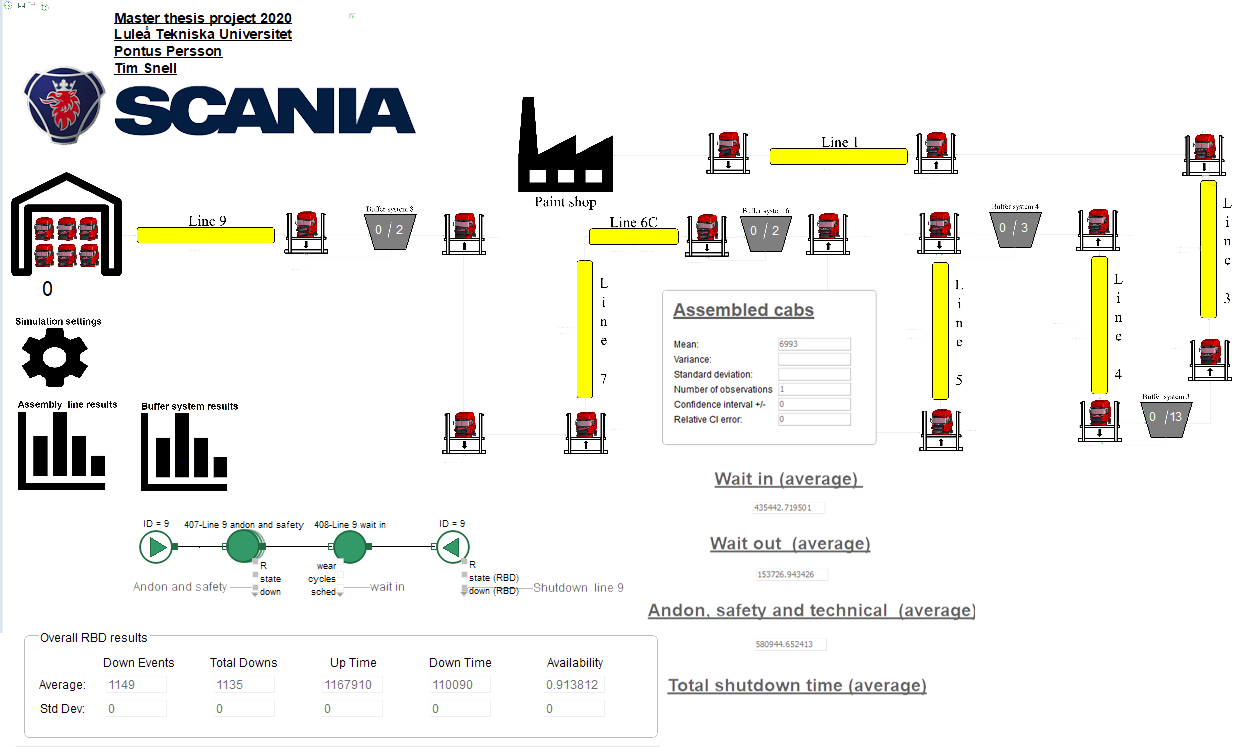 A master thesis within mechanical engineering performed by two students has been conducted at Scania in Oskarshamn. The purpose has been to investigate if Discrete Event Simulation using ExtendSim can be applied to increase Scania's assembly productivity. The objective was to investigate how buffer systems could be managed by varying the amount of buffers and their transport speed. Assembly line takt times with regard of their availability was also investigated. The method of approach was to build a simulation model to gain valid decision making information regarding these aspects. Process stop data was extracted and imported to ExtendSim where the Reliability library was used to generate shutdowns.
A master thesis within mechanical engineering performed by two students has been conducted at Scania in Oskarshamn. The purpose has been to investigate if Discrete Event Simulation using ExtendSim can be applied to increase Scania's assembly productivity. The objective was to investigate how buffer systems could be managed by varying the amount of buffers and their transport speed. Assembly line takt times with regard of their availability was also investigated. The method of approach was to build a simulation model to gain valid decision making information regarding these aspects. Process stop data was extracted and imported to ExtendSim where the Reliability library was used to generate shutdowns.
Comparing 24 sets over 100 runs to each other a median standard deviation of 0,91 % was achieved. Comparing the total amount of assembled cabs over a time period of five weeks with the real time data a difference of 4,77 % was achieved. A difference of 1,85 % in total amount of shutdown time was also achieved for the same conditions.
The biggest effect of varying buffer spaces was for system 6A. An increasement of up to 20 more assembled cabs over a time period of five weeks could then be achieved. By increasing all the buffer transport speeds by 40 %, up to 20 more assembled cabs over a time period of five weeks could be achieved. A push and pull system was also investigated where the push generated the best results. A 22 hour decreasement of total shutdown time and an increasement of 113 more assembled cabs over a time period of five weeks could be achieved.
Approach
The plan was to first build a digital twin of an assembly production. Once the digital twin was built and validated, different scenarios could be evaluated to answer questions such as:
- What is the most optimal state of the buffer system?
- How can TTR and TBF of assembly stations be optimized and what are the affects?
To accomplish this, researchers built a process map, a conceptual model, and a digital twin. After gathering process data they could evaluate different scenarios.
Stoppage times was used to define TTR and TBF which was essential for creating a valid model. Therefore, the ExtendSim Reliability library was an essential part of this project.
Results and Conclusions
- The simulation model generates viable decision making information, therefore fulfills its purpose.
- The simulation model produces results with a median standard deviation of 0,91 % for 24 sets over 100 runs with the same settings.
- The total amount of assembled cabs differ by 4,77 % between the simulation model and weekly statistical reports.
- The total shutdown time differ by 1,85 % between the simulation model and Power BI.
- The simulation model is accurate for the current assembly process and can be used within Scania in the near future.
- By increasing the amount of spaces for buffer system 6A an increasement of assembled cabs up to 20 is achieved for a time period of five weeks. A positive trend by increasing the amount of spaces for buffer system 1 and 3 can be seen.
- By increasing all the buffer transport speeds by 40 %, up to 20 more cabs are assembled over a time period of five weeks.
- A push production system lowers the total shutdown time by 22 hours over a time period of five weeks compared with the current state.
- A push production system increases the amount of assembled cabs by 113 over a time period of five weeks compared to the current state.
Education • Optimizing Performance of Educational Processes
 Higher Education Management in Relation to Process Organization Theory
Higher Education Management in Relation to Process Organization Theory
Maja Cukusic
University of Split
PhD in Business Informatics • March 2011
Project published as
"Online self-assessment and students' success in higher education institutions"
Maja Ćukušić, Željko Garača, Mario Jadrić
Computers & Education - An International Journal
March 2014 • ISSN 0360-1315
Abstract
 This paper validates effects of online self-assessment tests as a formative assessment strategy in one of the first year undergraduate courses. Achieved students' results such as test scores and pass rates are compared for three different generations for the same course but also judged against the exam results of other courses taught in the same semester. The analysis points out that there is a statistically significant difference between the groups for half-semester tests and exam pass rates after online self-assessment tests were introduced. Positive effects on students' success are approximated for the overall institution using a simulation model. Results point out that a small increase in pass rates could significantly impact the overall success i.e. decrease of dropout rates.
This paper validates effects of online self-assessment tests as a formative assessment strategy in one of the first year undergraduate courses. Achieved students' results such as test scores and pass rates are compared for three different generations for the same course but also judged against the exam results of other courses taught in the same semester. The analysis points out that there is a statistically significant difference between the groups for half-semester tests and exam pass rates after online self-assessment tests were introduced. Positive effects on students' success are approximated for the overall institution using a simulation model. Results point out that a small increase in pass rates could significantly impact the overall success i.e. decrease of dropout rates.
The research model that preceded the simulation explored the correlation between ICT support of educational processes and their outcomes. In order to test the impact of ICT support a sub-process was chosen: extensive self-evaluation quizzes delivered via e-learning system were designed, implemented and monitored within a first-year university course. The results were controlled and measured with regards to students’ outcomes achieved during the previous and current academic year in several courses (horizontal and vertical control of the results). Given the correlations between variables that characterize support of the educational process and outcomes on tests and exams, ICT support of the educational process has a positive effect as expressed in terms of relevant performance indicators.
A simulation model was developed which allows extrapolation of the impact on key performance indicators (i.e. drop-out rate and study completion time) for the whole institution enabling analysis of potential opportunities. The model adheres to study regulations of the Faculty of Economics (University of Split) and simulates outcomes for a generation of undergraduate students. Simulated results were compared with the actual data from the information system to verify the correctness of the model.
Not all course environments allow implementation of self-evaluation quizzes that result in slightly better exam pass-rate (roughly about 3%). Consequently, the simulation experiment investigates the process change for only half of the courses and only for the largest group of students (60%). As a result, the percentage of students who drop out from their studies could be significantly lower, 36% compared to 45.67% in real-life. For the entire system, this relatively small per-course improvement in exam results has a strong overall effect.
 download paper (in English)
download paper (in English)
 download paper (in Croatian)
download paper (in Croatian)
Other Publications by this Researcher
For a complete list of publications by Maja Ćukušić, please go to http://bib.irb.hr/lista-radova?autor=300571.
Feedstock Supply Chain for Biofuels and Biochemicals
 Integrated Simulation Modeling for Supply Chain Impacts of Genetic Improvements in Switchgrass
Integrated Simulation Modeling for Supply Chain Impacts of Genetic Improvements in Switchgrass
Haley Stauffer
Pennsylvania State University
Masters of Science in Agricultural and Biological Engineering • July 2020
Abstract
 The implementation of advanced lignocellulosic biofuel production in the U.S. is largely dependent on identifying and addressing uncertainty and risk along the feedstock supply chain. Switchgrass is a warm season herbaceous perennial grass native to North America that is well suited for biofuel production, according to the Department of Energy (DOE). This proposed research will evaluate the impacts on the supply chain from improved switchgrass phenotypes, accounting for increased yield and better yield stability. Data will be taken from the daily time-step biogeochemical model, DayCent, and incorporated into a supply chain model, ExtendSim Pro, via Python, quantifying risks along different regional supply chains. The results generated from these integrated models will enable better informed current and future decision making regarding the U.S. switchgrass bioenergy supply chain for growers, processors, and policy makers alike.
The implementation of advanced lignocellulosic biofuel production in the U.S. is largely dependent on identifying and addressing uncertainty and risk along the feedstock supply chain. Switchgrass is a warm season herbaceous perennial grass native to North America that is well suited for biofuel production, according to the Department of Energy (DOE). This proposed research will evaluate the impacts on the supply chain from improved switchgrass phenotypes, accounting for increased yield and better yield stability. Data will be taken from the daily time-step biogeochemical model, DayCent, and incorporated into a supply chain model, ExtendSim Pro, via Python, quantifying risks along different regional supply chains. The results generated from these integrated models will enable better informed current and future decision making regarding the U.S. switchgrass bioenergy supply chain for growers, processors, and policy makers alike.
Approach
The research strategy involved utilizing the existing framework for supply chain modeling of poplar conducted by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and implementing the mass and energy metrics with respect to switchgrass. Mass and energy inputs were gathered for the ExtendSim model to determine the cost points in which a certain switchgrass phenotype would prove more advantageous environmentally (yield, yield stability, drought resistance) and economically. Selected equipment was incorporatedat different stages along with their presumed quantity for the regional field case studies (Tennessee, Pennsylvania, and Iowa). Costs for this equipment as well as energy usage in addition to sorting through the supply shortage or supply surplus scenarios as they relate to costs were also modeled.
Results and Conclusions
 Ms. Stauffer was awarded first place in the poster competition at the Northeast Agricultural and Biological Engineering Conference (NABEC) for her work on this project.
Ms. Stauffer was awarded first place in the poster competition at the Northeast Agricultural and Biological Engineering Conference (NABEC) for her work on this project.
ORNL will be utilizing this data to further their efforts in industrial scale research of bioenergy production from switchgrass. This thesis provides an academic addition to the existing literature to better improve further knowledge of switchgrass supply chain needs and management.
Forest Machine Systems
 Comparison Between a Two-Machine System and Komatsu X19 Harwarder
Comparison Between a Two-Machine System and Komatsu X19 Harwarder
Petter Berggren & Philip Öhrman
Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences
Bachelor in Forest Technology • September 2017
Abstract
 Today, commercial forestry almost exclusively uses a two-machine system where the harvester fells, twigs, cuts, and sorts the wood on the ground. It is then picked up by a forwarder which transports the wood from the forest to the road. The system is proven and has been developed for decades. Earlier attempts for efficiency have beeen made with another type of system where a harwarder manages the entire process, primarily at thinning. Komatsu has developed a new harwarder (X19) that focuses on final fellings and this machine is the basis for this study. The work has been to model and run simulations in ExtendSim with time studies of the two competing systems. The aim of the simulation is to find out if, when and in which cases, how well the harwarder can compete with the current two-machine system.
Today, commercial forestry almost exclusively uses a two-machine system where the harvester fells, twigs, cuts, and sorts the wood on the ground. It is then picked up by a forwarder which transports the wood from the forest to the road. The system is proven and has been developed for decades. Earlier attempts for efficiency have beeen made with another type of system where a harwarder manages the entire process, primarily at thinning. Komatsu has developed a new harwarder (X19) that focuses on final fellings and this machine is the basis for this study. The work has been to model and run simulations in ExtendSim with time studies of the two competing systems. The aim of the simulation is to find out if, when and in which cases, how well the harwarder can compete with the current two-machine system.
Approach
Two different forest machine systems deliver roundwood to roadside. The traditional system consists of two machines: a harvester (felling trees) and a forwarder (hauling trees to roadside). The single-machine system consists of a harwarder, doing both felling and hauling. Our research compares the productivity and economy between the two systems.
The goal was to update old results from research in this area with new knowledge using data from modern machines, taking advantage of the opportunities for discrete-event simulation modelling in ExtendSim.
Results and Conclusions
Simulation results show that the harwarder has significantly lower process costs during small projects with short terrain transport distances. This is mainly due to the transport costs of the machines and that the harwarder reduces time during loading while cutting the logs, unlike the two-machine system, directly to the cargo carrier.
Other Publications by this Researcher
B. Talbot , T. Nordfjell & K. Suadicani. "Assessing the Utility of Two Integrated Harvester-Forwarder Machine Concepts Through Stand-Level Simulation". International Journal of Forest Engineering (2003), 14:2, 31-43
ExtendSim had been used in a Doctoral thesis at SLU: Eriksson, Anders. "Improving the Efficiency of Forest Fuel Supply Chains". Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences. Department of Energy and Technology. (2016).
Healthcare • Emergency Department Crowding
 The Financial Consequences of Lost Demand and Reducing Boarding in Hospital Emergency Departments
The Financial Consequences of Lost Demand and Reducing Boarding in Hospital Emergency Departments
Bob Batt
University of Pennsylvania • Wharton School
PhD in Operations Management • April 2011
Project published in and presented at
 Results of Mr. Batt's project was published in the Annals of Emergency Medicine in October 2011. The American College of Emergency Physicians thought the findings were so significant that they issued a press release about the paper. The main find was that reducing emergency department boarding by one hour could generate approximately $2.7M per year if dynamic admitting policies are used to control elective patient arrivals.
Results of Mr. Batt's project was published in the Annals of Emergency Medicine in October 2011. The American College of Emergency Physicians thought the findings were so significant that they issued a press release about the paper. The main find was that reducing emergency department boarding by one hour could generate approximately $2.7M per year if dynamic admitting policies are used to control elective patient arrivals.  This is a novel finding in that no previous work has put together the revenue gains from the ED of reducing boarding with the potential revenue reductions from reducing elective patients. Mr. Batt presented this paper at the Production & Operations Management Society conference Conference in Reno, Nevada on April 29, 2011.
This is a novel finding in that no previous work has put together the revenue gains from the ED of reducing boarding with the potential revenue reductions from reducing elective patients. Mr. Batt presented this paper at the Production & Operations Management Society conference Conference in Reno, Nevada on April 29, 2011.
Abstract
 This project explores the operational ramifications of crowding in hospital emergency departments. A common indicator of crowding is patients “boarding” in the emergency department while awaiting transfer to an inpatient bed in the hospital. Boarding is a controversial topic in the medical community because it has been suggested that it is a way to tacitly prioritize high-dollar elective patients over lower-value emergency patients. However, the financial impact of boarding is not obvious since boarding creates congestion in the emergency department leading to higher levels of lost demand from patients leaving without treatment and ambulances being diverted. We use discrete event simulation to model a hospital under various boarding regimes and patient prioritization schemes. We find that reducing boarding can be not only operationally efficient but also financially beneficial for the hospital.This project explores the operational ramifications of crowding in hospital emergency departments. A common indicator of crowding is patients “boarding” in the emergency department while awaiting transfer to an inpatient bed in the hospital. Boarding is a controversial topic in the medical community because it has been suggested that it is a way to tacitly prioritize high-dollar elective patients over lower-value emergency patients. However, the financial impact of boarding is not obvious since boarding creates congestion in the emergency department leading to higher levels of lost demand from patients leaving without treatment and ambulances being diverted. We use discrete event simulation to model a hospital under various boarding regimes and patient prioritization schemes. We find that reducing boarding can be not only operationally efficient but also financially beneficial for the hospital.
This project explores the operational ramifications of crowding in hospital emergency departments. A common indicator of crowding is patients “boarding” in the emergency department while awaiting transfer to an inpatient bed in the hospital. Boarding is a controversial topic in the medical community because it has been suggested that it is a way to tacitly prioritize high-dollar elective patients over lower-value emergency patients. However, the financial impact of boarding is not obvious since boarding creates congestion in the emergency department leading to higher levels of lost demand from patients leaving without treatment and ambulances being diverted. We use discrete event simulation to model a hospital under various boarding regimes and patient prioritization schemes. We find that reducing boarding can be not only operationally efficient but also financially beneficial for the hospital.This project explores the operational ramifications of crowding in hospital emergency departments. A common indicator of crowding is patients “boarding” in the emergency department while awaiting transfer to an inpatient bed in the hospital. Boarding is a controversial topic in the medical community because it has been suggested that it is a way to tacitly prioritize high-dollar elective patients over lower-value emergency patients. However, the financial impact of boarding is not obvious since boarding creates congestion in the emergency department leading to higher levels of lost demand from patients leaving without treatment and ambulances being diverted. We use discrete event simulation to model a hospital under various boarding regimes and patient prioritization schemes. We find that reducing boarding can be not only operationally efficient but also financially beneficial for the hospital.
Healthcare • Hospital Prep for a Mass Casualty Event
 Assessing Hospital System Resilience to Events Involving Physical Damage and Demand Surge
Assessing Hospital System Resilience to Events Involving Physical Damage and Demand Surge
Bahar Shahverdi, Mersedeh Tariverdi, Elise Miller-Hooks
George Mason University • Department of Civil, Environmental, and Infrastructure Engineering
PhD in Transportation • July 2019
PhD Dissertation Published In
 Socio-Economic Planning Sciences
Socio-Economic Planning Sciences
July 25, 2019
Highlights:
- Investigates potential benefits of hospital coalitions in a disaster.
- Assesses the potential value of patient transfers and resource sharing.
- Considers joint capacity enhancement alternatives.
- Discrete event simulation conceptualization of hospital system.
- Quantifies hospital system resilience to pandemic, MCI, and disaster events with damage.
Abstract
 This paper investigates the effectiveness of formalized collaboration strategies through which patients can be transferred and resources, including staff, equipment and supplies, can be shared across hospitals in response to a disaster incident involving mass casualties and area-wide damage. Inflicted damage can affect hospital infrastructure and its supporting lifelines, thus impacting capacity and capability or, ultimately, services that are provided. Using a discrete event simulation framework and underlying open queuing network conceptualization involving patient flows through 9 critical units of each hospital, impacts on critical resources, physical spaces and demand are modeled and the hospital system's resilience to these hazard events is evaluated.
This paper investigates the effectiveness of formalized collaboration strategies through which patients can be transferred and resources, including staff, equipment and supplies, can be shared across hospitals in response to a disaster incident involving mass casualties and area-wide damage. Inflicted damage can affect hospital infrastructure and its supporting lifelines, thus impacting capacity and capability or, ultimately, services that are provided. Using a discrete event simulation framework and underlying open queuing network conceptualization involving patient flows through 9 critical units of each hospital, impacts on critical resources, physical spaces and demand are modeled and the hospital system's resilience to these hazard events is evaluated.
Approach
ExtendSim was used to model individual hospitals as well as a small health care network. Initially, all possible patient routes in the hospitals (with different Trauma levels) were modeled first. Then, performance measures in different collaboration scenarios were analyzed.
Results and Conclusions
Findings from numerical experiments on a case study involving multiple hospitals spaced over a large metropolitan region replicating a system similar to the Johns Hopkins Hospital System show the potential of strategies involving not only transfers and resource sharing, but also joint capacity enhancement alternatives to improve post-disaster emergency health care service delivery through joint action.
Other Publications, Reports, & Projects from this Team
Rivinius, Jessica. "Engineered for Resilience" START, The National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism. July 25,2016.
TariVerdi M., Miller-Hooks E., Adan M. "Assignment Strategies for Real-Time Deployment of Disaster Responders" International Journal of Operations and Quantitative Management, Special Issue on Humanitarian Operations Management. January 2015.
Mollanejad M., Faturechi R., TariVerdi M., Kim M.. "A Generic Heuristic for Maximizing Inventory Slack in the Emergency Medication Distribution Problem". Transportation Research Board 93 Annual Meeting, Washington D.C. 2014.
Healthcare • Nanomedicine
 Nanomedicine
Nanomedicine
Janet Cheung
University of Southern California
Non-profit research project • January 2015
Project details
As part of a completely non-profit research project organized by our advisor, we aimed to answer the question of how effective the methodology of using nanobots can be for curing cancer as compared to the existing cancer drug because nanobots could integrate the diagnosis and treatment of cancer in a cohesive, potentially non-invasive unit through precise, targeted operations on the cellular level.
The key problems of conventional technology are the methods of drug delivery and the concentration of the drug cocktail required to destroy the cancerous cells. So nanobots would potentially allow the drugs to be directed to exact location where cancerous cells have been observed. Thus, only the malignant tissues are affected, and healthy tissues are not. As a result, nanomedicine does have the potential to revolutionize the way medicine is practiced around the world, but it is clear that biocompatibility on the nanoscale is one of many major challenges that must be overcome.
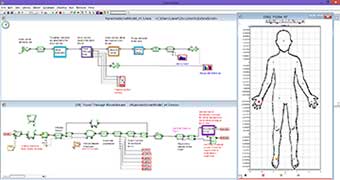 The model created focuses on drug delivery via the bloodstream (which is the most common and preferred method of delivery). It has the skeletons for active and passive targeting nanobots. The nanobots simulate flowing through the bloodstream until it is attracted to the tumor. Additionally, the model accounts for various possible drug delivery failures (i.e. early deployment of the drug, power failure, and time constraints). For now, the model determines when the failures occur using various probability distributions as placeholders for more legitimate values. Upon failure, the representation of the nanobot exits the model. The number of each type of failure can be viewed in a bar graph. In the event of a successful nanobot to tumor attachment, the representative nanobot in the model incurs latency, which accounts for attaching to the tumor and actual drug deployment. The number of successful deliveries to the number of failed deliveries can be seen in another bar graph available.The model focuses on drug delivery via the bloodstream (which is the most common and preferred method of delivery). It has the skeletons for active and passive targeting nanobots. The nanobots simulate flowing through the bloodstream until it is attracted to the tumor. Additionally, the model accounts for various possible drug delivery failures (i.e. early deployment of the drug, power failure, and time constraints). For now, the model determines when the failures occur using various probability distributions as placeholders for more legitimate values. Upon failure, the representation of the nanobot exits the model. The number of each type of failure can be viewed in a bar graph. In the event of a successful nanobot to tumor attachment, the representative nanobot in the model incurs latency, which accounts for attaching to the tumor and actual drug deployment. The number of successful deliveries to the number of failed deliveries can be seen in another bar graph available.
The model created focuses on drug delivery via the bloodstream (which is the most common and preferred method of delivery). It has the skeletons for active and passive targeting nanobots. The nanobots simulate flowing through the bloodstream until it is attracted to the tumor. Additionally, the model accounts for various possible drug delivery failures (i.e. early deployment of the drug, power failure, and time constraints). For now, the model determines when the failures occur using various probability distributions as placeholders for more legitimate values. Upon failure, the representation of the nanobot exits the model. The number of each type of failure can be viewed in a bar graph. In the event of a successful nanobot to tumor attachment, the representative nanobot in the model incurs latency, which accounts for attaching to the tumor and actual drug deployment. The number of successful deliveries to the number of failed deliveries can be seen in another bar graph available.The model focuses on drug delivery via the bloodstream (which is the most common and preferred method of delivery). It has the skeletons for active and passive targeting nanobots. The nanobots simulate flowing through the bloodstream until it is attracted to the tumor. Additionally, the model accounts for various possible drug delivery failures (i.e. early deployment of the drug, power failure, and time constraints). For now, the model determines when the failures occur using various probability distributions as placeholders for more legitimate values. Upon failure, the representation of the nanobot exits the model. The number of each type of failure can be viewed in a bar graph. In the event of a successful nanobot to tumor attachment, the representative nanobot in the model incurs latency, which accounts for attaching to the tumor and actual drug deployment. The number of successful deliveries to the number of failed deliveries can be seen in another bar graph available.
The model also has toxicity and biocompatibility factored into it. The body has an assumed toxicity capacity, which is the level that it can contain the toxins and still be healthy. Each drug has its own toxicity level, which is inversely proportional to its biocompatibility. The nanobots release the toxins into the bloodstream per failed drug delivery, which gradually increases the current toxicity level in the body. As with the probability distributions for the drug delivery failures, I have implemented placeholder values. These placeholder values can all be easily replaced with more accurate values with further research.
Healthcare • Patient Flow
 Essays on Efficiency in Service Oeprations: Applications in Health Care
Essays on Efficiency in Service Oeprations: Applications in Health Care
John Norris
Purdue University
PhD in Management, Quantitative Methods • December 2007
Abstract
Partnering with Indiana University Medical Group (IUMG), the author focused on outpatient care:
- Address the issue of missed appointments.
- Analyze variability in patient flow.
- Analyze performance of phone system.
...to analyze and improve patient flow at an outpatient clinic of the Indiana University Medical Group. Queuing concepts were used to uncover sources of variability and to generate ideas to improve clinic operations that would mitigate the undesirable effect of variability. 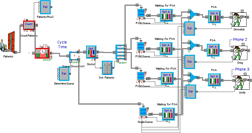 A process map, that matched the process at the clinic, was developed and validated. Data on task times was collected by observing the process with stopwatch or from historical records. A simulation model corresponding to the process map was developed, and the output was validated. Several ideas to modify clinic operations were tested on the validated simulation model. The overall result was an improvement in both the mean and the standard deviation of patient wait time, as well as higher utilization of physicians’ time. The clinic has implemented several of their recommendations and experienced improvements consistent with model predictions.
A process map, that matched the process at the clinic, was developed and validated. Data on task times was collected by observing the process with stopwatch or from historical records. A simulation model corresponding to the process map was developed, and the output was validated. Several ideas to modify clinic operations were tested on the validated simulation model. The overall result was an improvement in both the mean and the standard deviation of patient wait time, as well as higher utilization of physicians’ time. The clinic has implemented several of their recommendations and experienced improvements consistent with model predictions.
![]() Healthcare • Policy Setting for Operating Room Management
Healthcare • Policy Setting for Operating Room Management
 Improving surgical service delivery: Managing surgery cancellations with comprehensive scheduling and simulation of operating room capacity management policie
Improving surgical service delivery: Managing surgery cancellations with comprehensive scheduling and simulation of operating room capacity management policie
Mona Koushan
Otago University
PhD in Management • December 2021
Supervised by: Lincoln Wood
Abstract
This doctoral thesis investigates how to improve surgical service delivery by managing surgery cancellations through better scheduling and operating room (OR) capacity management. The research is structured around three main studies: a systematic review of surgery cancellations, the development of a robust scheduling model, and the evaluation of OR capacity management policies using simulation.
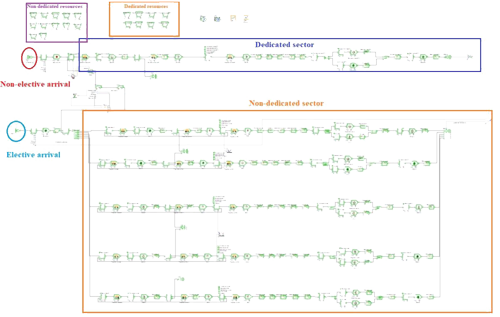 ExtendSim played a central role in the third study, which evaluated different operating room capacity management (ORCM) policies. An ExtendSim model was developed to simulate patient flows and resource utilization under various policy scenarios. The model enabled detailed scenario testing, supporting evidence-based policy decisions without disrupting real-world operations. The simulation model incorporated:
ExtendSim played a central role in the third study, which evaluated different operating room capacity management (ORCM) policies. An ExtendSim model was developed to simulate patient flows and resource utilization under various policy scenarios. The model enabled detailed scenario testing, supporting evidence-based policy decisions without disrupting real-world operations. The simulation model incorporated:
- Patient flow logic for both elective and non-elective surgeries, including upstream (pre-op), OR, and downstream (recovery/ICU) stages.
- Resource constraints (beds, staff, ORs) and stochastic elements (surgery durations, emergency arrivals).
- Policy scenarios: dedicated, flexible, and hybrid ORCM policies, each with different allocations of ORs to elective and emergency cases.
- Scheduling approaches: both simple (OR-focused) and comprehensive (including upstream/downstream resources and uncertainties).
The simulation was parameterized using published data (mainly from New Zealand hospitals) and allowed for sensitivity analyses on hospital size, scheduling policy, and resource levels.
The systematic review found that most cancellations are due to hospital-related causes (e.g., lack of OR time, scheduling issues, bed shortages), which are controllable by management. Improved coordination and scheduling can significantly reduce cancellations.
A new multi-objective scheduling model was developed to optimize:
- OR overtime and idle time,
- Buffer times between surgeries (to absorb variability),
- Number of patients scheduled.
The model incorporated uncertainties in surgery duration and emergency arrivals, using robust optimization and metaheuristic algorithms.
Results
Model results showed that comprehensive scheduling (considering all resources and uncertainties) outperformed simpler models, increasing patient throughput and reducing cancellations and overtime. ExtendSim simulations demonstrated that the effectiveness of ORCM policies depends on hospital circumstances (size, case mix, resource levels). No single policy is universally optimal:
- Flexible policies (shared ORs for electives and emergencies) generally performed best in larger hospitals, reducing cancellations and improving utilization.
- Hybrid policies (some dedicated, some flexible ORs) offered a good balance for medium-sized hospitals.
- Dedicated policies (separate ORs for emergencies) were less efficient, especially in smaller hospitals.
Comprehensive scheduling further improved the performance of all policies, especially when combined with flexible or hybrid ORCM approaches. Sensitivity analyses showed that increasing ICU beds (not just ORs) had the greatest impact on increasing the number of surgeries performed.
Conclusion
ExtendSim was instrumental in modeling and analyzing complex hospital operations, allowing the researcher to test and compare the impact of different scheduling and capacity management strategies. The results highlight the importance of comprehensive, system-wide coordination and the need to tailor policies to hospital-specific factors. The simulation findings offer actionable guidance for reducing surgery cancellations and improving resource utilization in surgical services.
Healthcare • Public Health
 Choosing Number and Scheduling Priority of Warm-hand Offs: A DES Model
Choosing Number and Scheduling Priority of Warm-hand Offs: A DES Model
Evelyn Cumberbatch
Yale University
Masters Thesis for Yale School of Public Health • May 2014
Abstract
The integration of behavioral health care into primary care is being promoted as a means to treat more people with behavioral health problems where they are most likely to be seen. Clinics with traditional behavioral health services may open slots among scheduled appointments to see these "warm-hand off" (WHO) patients identified by primary care providers (PCPs). The effects of giving priority for behavioral health appointments to either scheduled or WHO patients and of the number of appointments left open for WHO patients are investigated in this project.
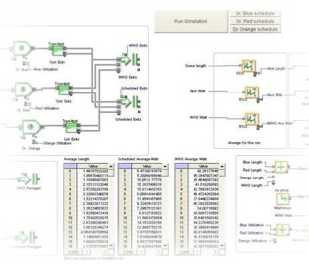 A discrete event simulation model was built of a moderately integrated clinic. WHO patients arrive randomly, on average 4 per day per PCP, and wait to see behavioral health providers (BHPs) who also see scheduled patients. Simulations of four clinic sizes, with PCP to BHP ratios of 1:1, were run. Effects of queue discipline (priority is given to scheduled or WHO patients) and the number of open WHO slots (3 or 5) are analyzed. Outcomes include the percent of scheduled patients served, the percent of WHO patients served, and the percent of BHP utilization.
A discrete event simulation model was built of a moderately integrated clinic. WHO patients arrive randomly, on average 4 per day per PCP, and wait to see behavioral health providers (BHPs) who also see scheduled patients. Simulations of four clinic sizes, with PCP to BHP ratios of 1:1, were run. Effects of queue discipline (priority is given to scheduled or WHO patients) and the number of open WHO slots (3 or 5) are analyzed. Outcomes include the percent of scheduled patients served, the percent of WHO patients served, and the percent of BHP utilization.
In clinics with 1 PCP and 1 BHP, for 3 and 5 open slots respectively, giving priority to WHO patients resulted in 80.6% and 81.0% of WHO patients served and 84.4% and 86.6% of scheduled patients served, however, giving priority to scheduled patients resulted in 97.8% and 98.1% of scheduled patients served, but 32.0% and 47.9% of WHO patients served. A similar pattern was seen for larger clinics, though the percent of WHO patients served increased for both 3 and 5 open slots with clinic size. Having 3 or 5 open slots led to few differences when WHO patients were given priority, but when scheduled patients were given priority, choosing 5 open slots rather than 3 open slots, increased the percent of WHO patients served by 15-20 percentage points across the clinic sizes. In either queue discipline, changing from 3 to 5 open slots reduced the percent of BHP utilization by approximately 8 percentage points for all clinic sizes. When WHO patients were given priority, the average wait time for scheduled patients increased from approximately 2-5 minutes to 13-19 minutes across clinic sizes.
These results might suggest to some clinics attempting to integrate primary care and traditional behavioral health services to choose to give WHO patients priority. However, it is recognized that there are costs associated with not seeing both scheduled and WHO patients, and clinics making this decision will have to weigh these tradeoffs. The analysis of these results provides one framework to assist in choosing between different arrangements for integration.
 download ExtendSim paper and model
download ExtendSim paper and model
Other Publications by this Researcher
During Dr. Cumberbatch's psychiatry residency at University California, San Francisco:
Pole, N., Cumberbatch, E., et. al. "Comparisons Between High and Low Peritraumatic Dissociators in Cardiovascular and Emotional Activity While Remembering Trauma", Journal of Trauma and Dissociation, 2005; 6(4): 51-67.
Information Security
 Analyzing Security Decisions with Discrete Event Simulation
Analyzing Security Decisions with Discrete Event Simulation
Magnus Felde
Gjøvik University
Masters in Information Security • June 28, 2010
Abstract
As organizations become increasingly more dependent on information security in order to succeed, the security decisions made by the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) also becomes important and needs to be considered in the context of the organization. However, since the complexity of the organization's internal processes and the threats the organization is facing, the CISO needs a decision making tool or method in order to determine the effects of a specific security decision. Because of this, we have in this thesis determined the suitability of utilizing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Discrete Event Simulation (DES) as a method to help the CISO make the "best" security decision for his organization.
 The thesis is based on a health care specific scenario which has been constructed in collaboration with Akershus University Hospital (Ahus), Rheumatism Hospital at Lillehammer and Buypass. The scenario includes a patient treatment process and the processes related to the usage of smart cards and passwords as authentication mechanisms. Furthermore, KPIs which focuses on time usage and number of deviations has been identified, where deviations within this health care specific scenario relates to more traditional security incidents.
The thesis is based on a health care specific scenario which has been constructed in collaboration with Akershus University Hospital (Ahus), Rheumatism Hospital at Lillehammer and Buypass. The scenario includes a patient treatment process and the processes related to the usage of smart cards and passwords as authentication mechanisms. Furthermore, KPIs which focuses on time usage and number of deviations has been identified, where deviations within this health care specific scenario relates to more traditional security incidents.
A case study was then conducted based on the scenario. The results of this case study indicate no statistical significant difference between the two authentication mechanisms with regards to the average time a doctor uses on a business activity. However, based on the number of deviations identified, smart cards were determined the preferred security measure of the two.
In order to determine the suitability of the simulation approach, a second case study was also conducted. This second case study was based on the same scenario, but this time with a non-simulation approach. By comparing the process surrounding the two case studies, the non-simulation approach were determined the most cost-effective approach and the approach which provided the most direct link between the input data and the results. Based on this, the non-simulation approach was also determined the most suitable approach. However, we did determine that for "what if" analysis, the simulation approach becomes the best choice of the two.
Should a "what if" analysis be desirable, we have in this thesis proposed a new methodology which modelers can utilize in order to reduces the complexity of the model building process. The methodology, called Minimalistic Model Design (MIMD), excludes the temporal relationship between the identified business activities within the business process. This exclusion helps to reduce total time used on the model building process, and enables better scalability.
![]() Inventory Management • Smart Solutions in Inventory
Inventory Management • Smart Solutions in Inventory
 Implementing Smart Inventory System
Implementing Smart Inventory System
Akram Gamal, Jana Mohamed, Maram Kamal, Mohamed Anis, and Omar Shehab
Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport
Bachelor of Science in Industrial and Management Engineering • Arab Academy for Science, Technology, & Maritime Transport • July 2025
Supervised by: Prof. Khaled S. El-Kilany
Abstract
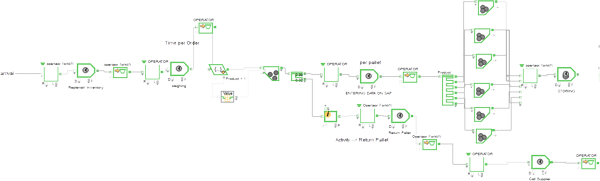 In response to inefficiencies caused by manual pallet tracking and verbal coordination at a warehouse facility, a real-time RFID-based inventory management system was introduced. The previous system led to delays, overworked staff, and poor resource utilization. By integrating RFID technology, the new system enables forklift operators to retrieve pallets directly from digital production plans, eliminating the need for manual searches and communication.
In response to inefficiencies caused by manual pallet tracking and verbal coordination at a warehouse facility, a real-time RFID-based inventory management system was introduced. The previous system led to delays, overworked staff, and poor resource utilization. By integrating RFID technology, the new system enables forklift operators to retrieve pallets directly from digital production plans, eliminating the need for manual searches and communication.
To evaluate the impact of this transformation, a simulation model was developed to compare the current and proposed systems. Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Analysis (MCDM) was used to select the most appropriate RFID components, balancing technical performance and cost. The results demonstrated a significant reduction in operator workload and cycle time, confirming the system’s effectiveness.
This initiative aligns with Industry 4.0 principles by enhancing traceability, visibility, and data-driven decision-making. The RFID system reduced operator utilization from 68% to 15% and cut average cycle time by 44%, showcasing its potential to streamline operations and improve inventory accuracy. Overall, the project highlights how digital transformation in inventory management can lead to smarter, faster, and more reliable industrial processes.
Results and Conclusions
The Industry 4.0 project represents a significant evolution in traditional inventory management through the integration of RFID technology. This initiative aims to enhance operational efficiency, minimize human intervention, and improve inventory accuracy. The transformation leads to smarter, faster, and more reliable inventory environments that can adapt to dynamic business needs. The RFID system plays a crucial role in advancing inventory operations by enabling real-time tracking of pallet locations, which reduces searching time, worker utilization, and overall cycle time. This system allows forklift workers to work independently on digital production plans received.
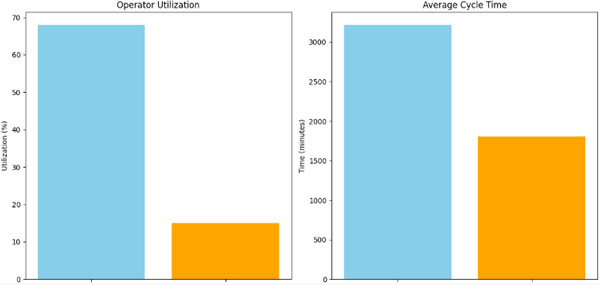 The implementation of the RFID system has led to significant efficiency improvements. Operator utilization decreased from 68% to 15%, representing a reduction of approximately 78%. Additionally, the average cycle time dropped from 3,217 minutes to 1,807 minutes, resulting in a reduction of approximately 44%. These metrics highlight the system's effectiveness in streamlining operations and accelerating process flow.
The implementation of the RFID system has led to significant efficiency improvements. Operator utilization decreased from 68% to 15%, representing a reduction of approximately 78%. Additionally, the average cycle time dropped from 3,217 minutes to 1,807 minutes, resulting in a reduction of approximately 44%. These metrics highlight the system's effectiveness in streamlining operations and accelerating process flow.
In conclusion, the use of RFID technology in inventory management offers various advantages, including process optimization, improved resource utilization, real-time tracking, and reduced cycle times. This technological advancement not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures that inventory environments are better equipped to meet the demands of modern business operations.
Kanban Approach in Software Development
 Limiting Work in Progress but Liberating Progress in Work; Utilising Process Simulation and Theories of Social Science to Understand the Value of Kanban for Software Development
Limiting Work in Progress but Liberating Progress in Work; Utilising Process Simulation and Theories of Social Science to Understand the Value of Kanban for Software Development
James Moriarty
National University of Ireland, Galway
Masters in Information Technology • August 2014
Abstract
"The Toyota Production System" first utilised just-in-time with Kanban as a method of visualising the work being completed. Inheriting from lean and agile software development philosophies, Kanban emerged for software development. The Kanban approach has few rules yet it is a powerful tool to evolve a software process.
 In this study, ExtendSim simulation software is used to model a Kanban approach. The ease of model creation and the potential for adaptability are both assessed. In addition, literature from social sciences are examined for evidence to support the benefits Kanban can bring to people in the software development process.
In this study, ExtendSim simulation software is used to model a Kanban approach. The ease of model creation and the potential for adaptability are both assessed. In addition, literature from social sciences are examined for evidence to support the benefits Kanban can bring to people in the software development process.
This study succeeded in creating a simulation of the Kanban approach for software development. A Kanban board was simulated to serve as a foundation from which other processes could be modelled accurately through modification or evolution. Lead time and cycle time indicate performance depending on the changes to work-in-progress limits of the various stages.
Evaluation of social science literature provides support for the human benefits associated with the implementation of Kanban. The simulation model provides meaningful data, but lacking real data prevents the model being broadly valid. Kanban and simulation appear to complement one another which is worthy of future study.
Lean Manufacturing
 Simulation of Lean Manufacturing Concepts using Extendsim Software
Simulation of Lean Manufacturing Concepts using Extendsim Software
Mark Young
Middle Tennessee State University
Engineering Technology • December 2012
Project description
In support of ET 6390 Lean Manufacturing, the visualization of core concepts for the class is important for increased comprehension. After polling the engineering and operations management curriculum about the use of simulation software, Mr. Young discovered it is not practiced on a frequent basis in either college at MTSU.
Using simulation software, specifically ExtendSim, as a tool for visualizing the push/pull/constrained WIP modeling, Mr. Young made the work available and in a form that, if so desired, could be readily adapted to the curriculum of ET 6390.
Project outcome
Mr. Young produced 3 videos for the course ET 6390 - Productivity Strategies/Lean Systems using ExtendSim:
- Simulating Little's Law with Penny Fab. Four identical tools in series.
- Penny Fab 2. Four stations with different processing times.
- Push & Pull Simulation. Side by Side Model.
Manufacturing • Creating a Production System
 Simulation of a Manufacturing Process - Military Aircrafts
Simulation of a Manufacturing Process - Military Aircrafts
Sandra Fors
Luleå Technical University
Master of Science in Engineering Technology • July 2016
Abstract
 The military aircraft manufacturing division at Saab Aeronautics is ready to enter the future of production systems and leap ahead in their field. Saab predicts an increase in demand of military aircrafts. To meet this new higher customer demand, this master's thesis is a part of a project to create a new production system.
The military aircraft manufacturing division at Saab Aeronautics is ready to enter the future of production systems and leap ahead in their field. Saab predicts an increase in demand of military aircrafts. To meet this new higher customer demand, this master's thesis is a part of a project to create a new production system.
Ms. Fors' Master's thesis includes following steps, each of which she thoroughly validated:
- A simulation model of a production system for military aircraft manufacturing.
- A system analysis and identification of bottlenecks through investigation of the queues in the simulation model.
- Testing of improvement suggestions.
- A simulation model which tests different production volumes.
- Recommendations for how to increase production volume by time, with solutions from two different development processes.
 The result of this thesis presents concepts on how to build a production system for military aircraft, including number of stations, improvement areas, and results of improvement suggestions on a general level. The simulation model created for this project presented the possibility to test a lot of scenarios and suggest improvements to find the best solution. The use of simulation software as an initial part of this project has proven successful and is recommended for use in the project in the future.
The result of this thesis presents concepts on how to build a production system for military aircraft, including number of stations, improvement areas, and results of improvement suggestions on a general level. The simulation model created for this project presented the possibility to test a lot of scenarios and suggest improvements to find the best solution. The use of simulation software as an initial part of this project has proven successful and is recommended for use in the project in the future.
Manufacturing • Using RFID Technology for Routing
 Evaluating the Impact of Introducing RFID Technology in Manufacturing Systems Using Simulation
Evaluating the Impact of Introducing RFID Technology in Manufacturing Systems Using Simulation
Aly Mohamed Owida
Arab Academy for Science, Technology, & Maritime Transport
Master of Science in Industrial and Management Engineering • May 2011
Project presented at
 41st International Conference on Computers and Industrial Engineering
41st International Conference on Computers and Industrial Engineering
October 23 to 26, 2011
Abstract
Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology has significant impact on product tracking and identification in manufacturing systems. Most of the business cases that implement the RFID technology in their operations have achieved various benefits. RFID technology can reduce the operating errors that affect the efficiency of the operations which results in improving different performance measures such as cycle time, throughput, work-in-process, resources utilization, and average waiting time in queues. In addition, several benefits such as improved items monitoring, lower lead times, and better inventory control can be achieved by introducing RFID technology. Recent developments in RFID technology and other supporting technologies have created opportunities for real-time traceability and better visibility inRadio frequency identification (RFID) technology has significant impact on product tracking and identification in manufacturing systems. Most of the business cases that implement the RFID technology in their operations have achieved various benefits. RFID technology can reduce the operating errors that affect the efficiency of the operations which results in improving different performance measures such as cycle time, throughput, work-in-process, resources utilization, and average waiting time in queues. In addition, several benefits such as improved items monitoring, lower lead times, and better inventory control can be achieved by introducing RFID technology. Recent developments in RFID technology and other supporting technologies have created opportunities for real-time traceability and better visibility inshop floor operations.
 This paper investigates the effectiveness of introducing RFID technology in tracking and identification processes for products flow in a job shop manufacturing facility. A leading furniture manufacturer in Egypt has been selected as a case study. The manufacturer produces a large number of customized furniture products. Errors in tracking and identification usually occur due to the large number of products present on the shop floor. Introduction of radio frequency identification technology at different stages of manufacturing is proposed to overcome these errors. Different simulation models have been developed for the post-assembly processes in the facility. These models have been developed with an intent to capture all the features that characterize a real furniture manufacturing facility. Simulation is used to assess the impact of introducing the RFID technology on a number of performance measures. Analysis and comparison of simulation results for the base and proposed models show that RFID implementation can improve the overall performance of the facility.
This paper investigates the effectiveness of introducing RFID technology in tracking and identification processes for products flow in a job shop manufacturing facility. A leading furniture manufacturer in Egypt has been selected as a case study. The manufacturer produces a large number of customized furniture products. Errors in tracking and identification usually occur due to the large number of products present on the shop floor. Introduction of radio frequency identification technology at different stages of manufacturing is proposed to overcome these errors. Different simulation models have been developed for the post-assembly processes in the facility. These models have been developed with an intent to capture all the features that characterize a real furniture manufacturing facility. Simulation is used to assess the impact of introducing the RFID technology on a number of performance measures. Analysis and comparison of simulation results for the base and proposed models show that RFID implementation can improve the overall performance of the facility.
Other Publications by this Researcher
A. M. Owida, K. S. El-Kilany, and A. E. El-Sayed. "Analytical Hierarchy Process for Selection of RFID System: An Application in Retail Supply Chains". Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Flexible Automation & Intelligent Manufacturing, 2010.
Neural Networks • SimNeural Technology
 SimNeural: Simulador Computacional de RNA para Aplicaçoes em Ensino e Pesquisas Medicas e Biologicas ("SimNeural: Computer Simulation of ANN for Learning and Research Purposes")
SimNeural: Simulador Computacional de RNA para Aplicaçoes em Ensino e Pesquisas Medicas e Biologicas ("SimNeural: Computer Simulation of ANN for Learning and Research Purposes")
Carlos Alberto Gonçalves
Joint collaboration through the Centre for E-Learning at both the University of Brasília and the University of Ottawa
PostDoc in Education and E-Learning • October 2013
Abstract
This research work is part of collaboration between the University of Brasilia (DF, Brazil) and the University of Ottawa (ON, Canada) and was carried out with other researchers from the University of Brasília: Bruno Bastos Neves, Jussie Marques Martins, and Wilson Henrique Veneziano. This project was designed to improve the quality of teaching materials of the former university with the know-how of the latter.
Computer simulation and pattern recognition by Artificial Neural Network (ANN) techniques has become an important tool for learning and professional purposes. This work reports the phases of design, development, and validation of the SimNeural software, that was conceived to be easy to use by professionals of Medical and Biological Sciences when working in research or learning purposes.
Computer simulation and pattern recognition by Artificial Neural Network (ANN) techniques has become an important tool for learning and professional purposes. This work reports the phases of design, development, and validation of the SimNeural software, that was conceived to be easy to use by professionals of Medical and Biological Sciences when working in research or learning purposes.
SimNeural was implemented in ExtendSim using the technique called component prototyping and recycling. SimNeural´s main objective is to be a framework where the user can easily configure and simulate models of ANN. For instance, it should be easy to implement hypothesis tests or to check the relationship among variables. To achieve that goal, the authors used ANN multilayer perceptrons and backpropagation learning. For the validation and test of this tool, they asked SimNeural to build and train some models.
This paper presents the following results:
- The ANN training phase that was used for the validation of the software.
- Sample analysis results.
- Experimental test results designed for pattern recognition and classification of real biological and medical databases.The results showed that SimNeural can be a useful and effective tool for applications at research and learning.
 download paper (available in Portuguese only)
download paper (available in Portuguese only)
Other Publications by this Researcher
Venezuano, W.H.; Rocha, A.F.; Goncalves, C.A.; Pena, A.J.; Carmo, J.C.; Nascimento, F.A.O.; Rainoldi, A. "Confounding factors in water EMG recordings: an approach to a definitive standard". Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, v. 44, p. 348-351, 2006.
Goncalves, C.A.; Cardoso, I.P.; Carvalho, T.C.; Freire, V.D. "Action Potential Propagation/Propagate do Potential". (CD-ROM, Simulation Software)/Publisher: Editorial Universidade de Brasilia, DF, Brazil, 2005.
Nogueira, E.L.; Correia, A.C.; Silva, R.A.; Goncalves, C.A.; Mota, Y.L. "Electromyographic assessment of the effect of age over paravertebral muscles/O efeito do envelhecimento nos mœsculos paravertebrais lombares investigado pela eletromiografia". In XI Congresso Brasileiro de Biomecica, 2005, Joo Pessoa. Anais do XI Congresso Brasileiro de Biomecnica, 2005. v. I. p. 1-4.
Cardoso, I.P.; Oliveira, C.C.S.; Freire, V.D.; Goncalves, C.A. "A methodology for building hypermedia courses in Physiology/Uma metodologia para desenvolver aulas em formato hiperm’dia para o ensino de fisiologia". In FeSBE2004-XIX Reunio da Federao de Sociedades de Biologia Experimental, 2004, çguas de Linda, Brazil, 2004.
Brasil-Neto, J.P.; Goncalves, C.A.; Lima, R.R.F.; Pessoa, V.F. "Development of a Computer-Based Method System for Studying Human Stereopsis: Contribution to the Study of Human Speed of Detection of Visual Depth". IEEE Computer Society, v. 1, p. 134-138, 1997.
Oil & Gas • Production Availability Analysis in Subsea Environments
 Production Availability Analysis: Implications on Modelling due to Subsea Conditions
Production Availability Analysis: Implications on Modelling due to Subsea Conditions
Tianqi Sun
Norwegian University of Science and Technology
Department of Ocean Operations and Civil Engineering
Masters in Production Assurance • June 2017
Abstract
 Subsea production and processing systems have become a hot topic among research institutes and industries. While highlighting the advantages on production and economy, the reliability issues show a different picture with limited access, difficulty of maintenance and possibly lower availability. The influence of these issues on the system performance is studied in this paper to evaluate the benefit of subsea systems.
Subsea production and processing systems have become a hot topic among research institutes and industries. While highlighting the advantages on production and economy, the reliability issues show a different picture with limited access, difficulty of maintenance and possibly lower availability. The influence of these issues on the system performance is studied in this paper to evaluate the benefit of subsea systems.
Approach
Production availability analysis has shown its potential in system optimization. Two main approaches, namely analytical and simulation, are used for analysis. ExtendSim was used in this process to reveal the use of the simulation approach and provide numerical results for this study. As subsea production continues to trend upward in the oil and gas industry, identifying the influencing factors and exploring how to conduct analysis in a subsea environment will be necessitated.
![]() Optimization • Multi-Product Powdered Mix Factory
Optimization • Multi-Product Powdered Mix Factory
 Optimization of Production Scheduling in a Multi-Product Powdered Mix Factory
Optimization of Production Scheduling in a Multi-Product Powdered Mix Factory
Adham Hendawy, Marwan Nagy, Farida Haytham, Justin Sameh, & Mayar Essam
Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport
Bachelor of Science in Industrial and Management Engineering • Arab Academy for Science, Technology, & Maritime Transport • July 2025
Supervised by: Prof. Khaled S. El-Kilany & Dr. Lina Ismail
Abstract
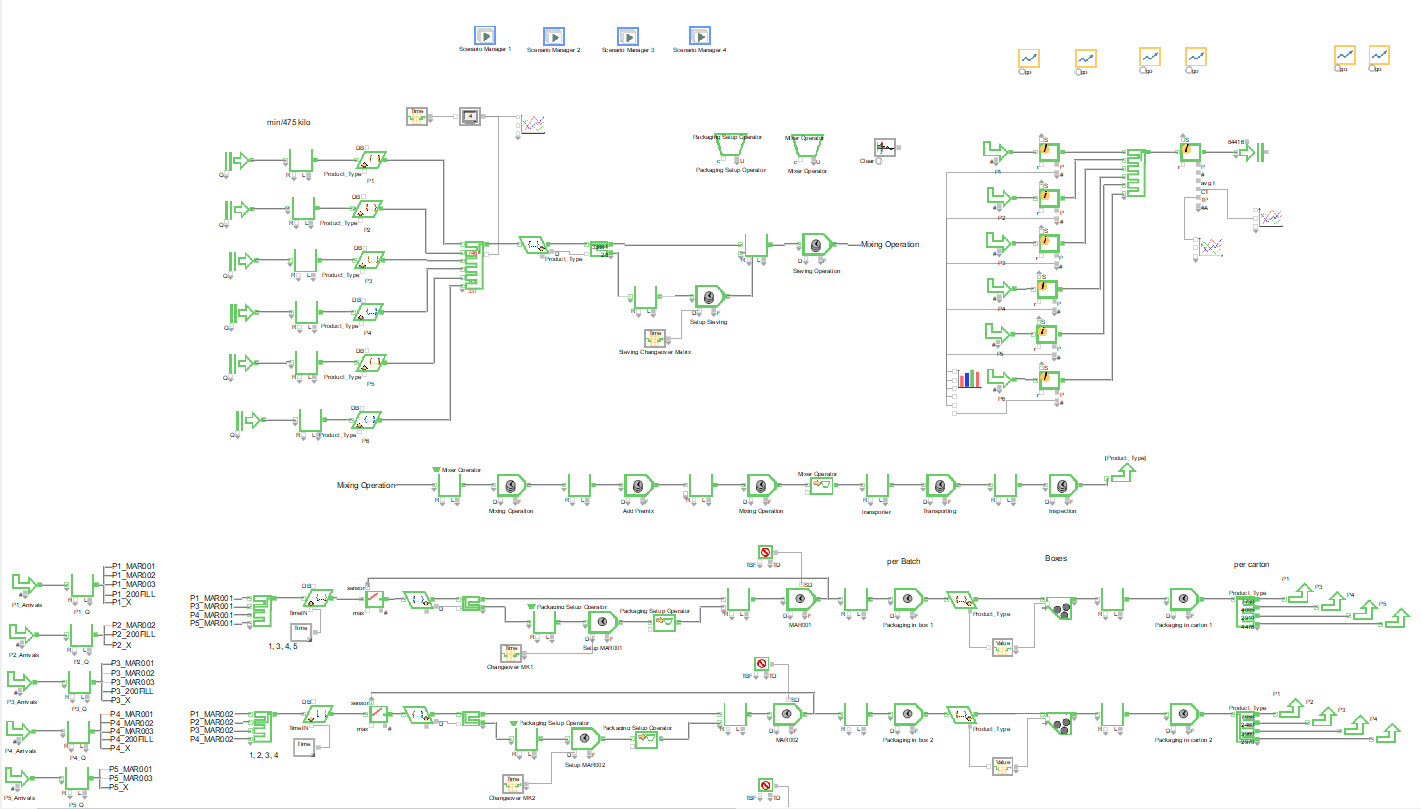 This paper focuses on improving production efficiency in a factory that manufactures over 400 powdered mix products, such as powder dessert mixes, instant powder drinks, ice cream mixes, and jelly desserts. The factory faces significant challenges related to bottlenecks and changeovers, especially with the recent addition of a new machine to the production line. The primary goals of this project were to:
This paper focuses on improving production efficiency in a factory that manufactures over 400 powdered mix products, such as powder dessert mixes, instant powder drinks, ice cream mixes, and jelly desserts. The factory faces significant challenges related to bottlenecks and changeovers, especially with the recent addition of a new machine to the production line. The primary goals of this project were to:
- Enhance production efficiency by evaluating different product sequencing strategies.
- Refine scheduling practices.
- Reduce idle times.
- Improve the integration of new machinery.
ExtendSim was used to build a simulation model designed to optimize how products are allocated to machines in a factory with sequence-dependent tasks.
Approach
The approach involved a detailed study of the factory's production process, including data collection on structural, operational, and numerical aspects. The production line was modeled using ExtendSim. The model incorporated various elements such as machine capacities, changeover matrices, and resource pools to reflect real-world conditions accurately. Multiple scenarios were tested to evaluate the impact of different product sequencing strategies on production performance. The scenarios included variations in product sequence, production time allocation, and seasonal demand shifts. Key performance metrics were analyzed, such as reducing changeover times, minimizing cycle times, resolving bottlenecks, and lowering WIP levels.
Results and Conclusions
The ExtendSim model identified that product sequence and changeover times significantly impact production performance. Testing 206 different scenarios revealed that adjusting the scheduling order can reduce cycle times and increase output. The optimal scenarios minimized downtime and improved workflow integration. Analysis revealed that by adjusting the scheduling order, it is possible to enhance system performance, increase throughput, and better meet customer demand. The study concluded that:
- Optimizing production scheduling can significantly improve overall efficiency by minimizing unnecessary changeovers and making better use of production time.
- Simulation models are valuable tools for testing and refining production strategies.
- Implementing lean scheduling methods such as Kanban or CONWIP could further enhance production flow and reduce delays.
Other Publications
Poster Presentation Event: Industrial Engineering Student Conference
Topic: Application of Lean Tools for Bottleneck Reduction in Manufacturing
Contribution: Presented research findings and practical applications of SMED and Kanban systems.
Collaborative Study (Planned)
Title: Improving Efficiency Through Simulation-Based Scheduling in Multi-Product Lines
Contribution: Assisted with case study analysis and ExtendSim model development.
![]() Packaging Line • Reducing Waste, Improving Efficiency, & Enabling Real-Time Quality Monitoring
Packaging Line • Reducing Waste, Improving Efficiency, & Enabling Real-Time Quality Monitoring
 Implementing Digital Kaizen in the Confectionery Industry
Implementing Digital Kaizen in the Confectionery Industry
Ameen Menessi, Amr Hossam, Jana Amr, Seif El Yassin, and Shady Ayman
Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport
Bachelor of Science in Industrial and Management Engineering • Arab Academy for Science, Technology, & Maritime Transport • August 2025
Supervised by: Prof. Khaled S. El-Kilany
Abstract
The report presents a comprehensive study on implementing Digital Kaizen in a gum and candy manufacturing facility in Egypt. The goal was to reduce waste, improve packaging line efficiency, and enable real-time quality monitoring. The project combined traditional lean tools (like Fishbone diagrams and Pareto analysis) with digital technologies such as Power BI dashboards and dynamic sampling systems. The study was conducted at Company X, a global leader in confectionery, and focused on its packaging line operations.
Use of ExtendSim for Simulation
ExtendSim was employed to simulate the packaging line under two configurations: the original (old) capacity and the expanded (new) capacity. The simulation model was built as a discrete-event system, incorporating real operational parameters such as machine rates, availability, Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), Mean Time to Repair (MTTR), and rework levels. The model replicated both primary and secondary packaging stages, including rework loops for defective units.
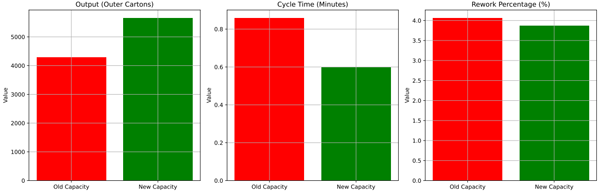 Old Capacity Simulation: Included six primary packaging machines and two secondary packaging machines. The simulation revealed a rework rate of 4.06%, a cycle time of 0.858 minutes per unit, and a total output of 4,289 outer cartons.
Old Capacity Simulation: Included six primary packaging machines and two secondary packaging machines. The simulation revealed a rework rate of 4.06%, a cycle time of 0.858 minutes per unit, and a total output of 4,289 outer cartons.- New Capacity Simulation: Expanded to eight primary packaging machines and four secondary packaging machines. Despite a higher number of reworked units, the rework percentage dropped to 3.87% due to increased throughput. Cycle times improved significantly—0.770 minutes for Line 1 and 0.424 minutes for Line 2—with total output rising to 5,653 outer cartons.
Results and Impact
The simulation analysis validated the effectiveness of the capacity expansion. Key outcomes included:
- A 31.8% increase in output.
- A 10.3% reduction in cycle time for Line 1 and a 50.6% reduction for Line 2.
- A 4.7% decrease in rework percentage.
These results confirmed that the expansion, supported by ExtendSim modeling, led to improved efficiency, better workload distribution, and enhanced responsiveness to market demands. The simulation also provided a data-driven foundation for decision-making and continuous improvement aligned with Digital Kaizen principles.
Papermaking • Machinery
 Simulation of a Paper Machine with the Simulation Software FlowMac
Simulation of a Paper Machine with the Simulation Software FlowMac
Joseph Niedermayer
Munich University of Applied Science
Masters in Papertechnology • January 2017
Abstract
Mr. Niedermayer used ExtendSim + FlowMac to build a simulation model to find weak parts or bottlenecks of a paper machine's wet end for the world leader in the design, development, and manufacturing of thinner, more sustainable, tailor-made speciality papers.
The model created precisely predicts mass flows helping the manufacturer to better understand the paper making process. They used the model to:
- Help determine the proper size of the mixing chest
- Realize the impact of different retention values during the simulation
- Evaluate white water consistency
- Determine the required mixing pump power to run a new quality on a machine
By request from the company, Mr. Niedermayer has changed the speed and grammage of the produced paper in the provided model to reflect it's proprietary content.
Perishable Product • Dynamic Pricing and Inventory Management
 Sustainable Dynamic Pricing for Perishable Food with Stochastic Demand
Sustainable Dynamic Pricing for Perishable Food with Stochastic Demand
Ghada Yehia Mostafa, N.M. Galal, K.S. El-Kilany
Arab Academy for Science, Technology, and Maritime Transport
Masters in Industrial Engineering • December 2018
Project presented at
 2018 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM)
2018 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM)
Bangkok, Thailand • December 16 to 19, 2018
Abstract
 In current competitive environment, retailers are facing a fierce competition and are aiming to manipulate customer purchasing attitudes. Dynamic pricing strategy is a major determinant of retailer’s profitability when considering perishable food. Furthermore, increasing pressure from society and international organizations calls for food security, safety and decreased food waste and losses. This paper investigates dynamic pricing strategy with the objective of maximizing revenue and minimizing food waste to ensure sustainability. A simulation model with stochastic demand based on product price and age is developed using ExtendSim Suite. The effect of inventory replenishment quantity on the performance measures is analyzed. Results reveal the superiority of dynamic pricing over fixed pricing strategy in terms of retailer profit and food waste.
In current competitive environment, retailers are facing a fierce competition and are aiming to manipulate customer purchasing attitudes. Dynamic pricing strategy is a major determinant of retailer’s profitability when considering perishable food. Furthermore, increasing pressure from society and international organizations calls for food security, safety and decreased food waste and losses. This paper investigates dynamic pricing strategy with the objective of maximizing revenue and minimizing food waste to ensure sustainability. A simulation model with stochastic demand based on product price and age is developed using ExtendSim Suite. The effect of inventory replenishment quantity on the performance measures is analyzed. Results reveal the superiority of dynamic pricing over fixed pricing strategy in terms of retailer profit and food waste.
Approach
The problem considered was to set the pricing strategy and inventory management of a perishable product in a retail store/supermarket. The nature of the item's deterioration and perishability impose two problems for the retailer. First, unsold quantities approaching or attaining its lifetime are wasted. Second, profit loss due to unsold items, which have been ordered, put in inventory and/or displayed. Customers are reluctant to buying products of less quality unless their price is reduced. Thus, the retailer needs to identify the dynamic price of the products according to its age in addition to how much inventory to order. The ultimate goal of setting the price and the quantity to order is to reduce waste, lost sales, and increase profit.
Results and Conclusions
Results revealed that when decreasing the inventory level, though almost no items deteriorate, still a loss in revenue occurs due to lost sales depending on customer demand. However, increasing the inventory level to meet all customers demand leads to an excess inventory and due to deteriorating nature of products they are wasted.
Furthermore, a comparison between fixed pricing strategy and dynamic pricing shows that the former is way less profitable for retailer, and more harmful for environment due to large perished quantities. In general, consumer refuses a fixed price for a product with decreasing quality, so dynamic pricing satisfies both the interest of retailer, customer, environment, and society.
Process Improvement • Increasing Throughput
 Screen Printing Scheduling Methodology
Screen Printing Scheduling Methodology
Brandon Wolfe & Kyle Naylor
California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo
Bachelor of Science in Graphic Communication • May 2010 completed
Project presented as
A Senior Project presented to the Faculty of the Graphic Communication Department
Abstract
 As the shift towards offhore business within the screen printing industry increases, American businesses must find a way to remain competitive. Due to manufacturing costs and regulation it is impossible for Americans to compete with the low per unit cost of foreign suppliers. By decreasing the time to market, American businesses will be able to remain competitive and recover lost business. In order to achieve this, a flexible scheduling model must be developed in order to increase throughput of a production process. This model serves to account for variables and variances that occur within the screen printing process, allowing for effective continuation of production.
As the shift towards offhore business within the screen printing industry increases, American businesses must find a way to remain competitive. Due to manufacturing costs and regulation it is impossible for Americans to compete with the low per unit cost of foreign suppliers. By decreasing the time to market, American businesses will be able to remain competitive and recover lost business. In order to achieve this, a flexible scheduling model must be developed in order to increase throughput of a production process. This model serves to account for variables and variances that occur within the screen printing process, allowing for effective continuation of production.
Results and Conclusions
After finishing the project, recommendations were made to engage students in the Graphic Communications department in learning the software and the fundamentals of the forward-thinking scheduling model. The basic program that was started has a lot of potential to be more dynamic and give more real-time analysis. The intent is to pass on the simulation to the department in hopes that it will continue to be built on and refined. Future projects along with this foundation model will serve to provide a valuable business tool for the screen printing industry. By implementing a forward thinking model along with visual representation software, printers will be able to remain competitive by improving their workflow and decreasing time to market.
Production Flow • Mapping Bottlenecks
 Kartläggning av flaskhalsar i ett nytt produktionsflöde genom simulering • En fallstudie genomförd på Duroc Rail AB
Kartläggning av flaskhalsar i ett nytt produktionsflöde genom simulering • En fallstudie genomförd på Duroc Rail AB
(Mapping bottlenecks in a new production flow through simulation • A case study carried out at Duroc Rail AB)
Rebecka Olsson
Lulea Technical University
Masters degree in Industrial Logistics • June 2023
Abstract.
 Duroc RailPresented in Swedish, this thesis is a case study carried out at Duroc Rail, a company in Luleå that maintains and processes railway wheels. Within the next four years, the entire operation will change premises as a result of changes in the industrial area where the company is located today. In connection with the move, a completely new production layout has been prepared. No calculations or simulations of the new production flow have been carried out at the time of the study and therefore it is difficult to ensure how the new production layout will work in reality and which bottlenecks may arise. The purpose of the study is therefore to, through a simulation, map the bottlenecks that may arise and investigate how these can be influenced and controlled.
Duroc RailPresented in Swedish, this thesis is a case study carried out at Duroc Rail, a company in Luleå that maintains and processes railway wheels. Within the next four years, the entire operation will change premises as a result of changes in the industrial area where the company is located today. In connection with the move, a completely new production layout has been prepared. No calculations or simulations of the new production flow have been carried out at the time of the study and therefore it is difficult to ensure how the new production layout will work in reality and which bottlenecks may arise. The purpose of the study is therefore to, through a simulation, map the bottlenecks that may arise and investigate how these can be influenced and controlled.
Overview.
 It is not often that a very complicated and expensive production flow is redesigned from scratch, which makes this an extraordinary opportunity to study which aspects should be taken into account in order to implement improvements against the previous production flow. Also the production line examined is not a manufacturing production but a production that maintains products. Hence, improvements are limited within a certain framework in that it is not possible to make changes in the product itself to make specific stations on the production line more efficient. The simulation is also done on a system that does not yet exist, which means that it is not possible to compare the result test in the simulation against reality, except against the old production line.
It is not often that a very complicated and expensive production flow is redesigned from scratch, which makes this an extraordinary opportunity to study which aspects should be taken into account in order to implement improvements against the previous production flow. Also the production line examined is not a manufacturing production but a production that maintains products. Hence, improvements are limited within a certain framework in that it is not possible to make changes in the product itself to make specific stations on the production line more efficient. The simulation is also done on a system that does not yet exist, which means that it is not possible to compare the result test in the simulation against reality, except against the old production line.
Results and Conclusions.
In its new production layout, Duroc Rail is recommended to follow, as much as possible, the new optimal intake routine developed by the study. The product mix should then be distributed with pairs of wheels in batches of two and with every third batch of the respective lathe line. If the optimal intake routine cannot be followed, it is important that the proportion of each wheel type does not exceed recommended limits and that the lathes are balanced to the highest possible degree.
The initial staffing grouping should be followed and it is important to follow a working method where operators are at the right workstation at the right time to ensure that any bottlenecks are not blocked as a result of the next workstation not having processed wheelsets and creating space in the buffer.
It is also important to understand that increasing performance on a workstation that is not a bottleneck does not result in any system-level improvements. There is no argument for lifting pairs of wheels out of tracks and setting them aside for the purpose of emptying a buffer that is not full or causing no blockages. To lift wheels out of a track is therefore not something that is recommended and should only be done in an emergency in abnormal situations.
In accordance with the staffing grouping proposed by Duroc Rail, a continued constant staffing of the sewing machine, both lathes and the blanking is recommended. Of the two operators who must man the ultrasound stations (UL1, UL2 and UL axis) on a shift, it is recommended that one operator always man UL2 as this station has a high degree of utilization and risks becoming a bottleneck. Furthermore, it is important to ensure that there are enough competent personnel who can perform the work at the ultrasound stations as well as a margin for possible absence. The same applies to the lathes and the sighting.
Duroc Rail is recommended to set aside space for an extra blanking machine in the new production layout. This will be necessary in case of an increase in demand. Even the time it takes to process a pair of wheels at the inspection must be improved if an increase in demand is made.
Furthermore, Duroc Rail is recommended to use the buffer sizes that were used as a starting point in the simulation for the new layout as these were sufficient to achieve the desired result with an optimal product mix according to the target picture. In order for the buffers to also cope with product mixes that do not follow the optimal product mix according to the target image, the buffer at station UL2 should be expanded from five to eight. The buffer on the cooling should also be increased to 36 to cope with increased demand and possible skewed product mix distributions.
Furthermore, the remaining initial buffer sizes are considered sufficient to handle a product mix that does not follow the optimum but that stays within the limits of what the production system can handle. The working method recommended for the new production layout is a working method that ensures that the buffer before a station always has the opportunity to receive a pair of wheels from a previous station that is under staffing. An extra focus should also be placed on the stations that are at risk of becoming bottlenecks, the lathes, the inspection, the emptying, UL2 and MT. Furthermore, processing at a station where the subsequent buffer is full must be paused if the subsequent station does not have a lower cycle time than the previous one.
Production Line • Flow Production
 Produktionsutveckling av Funktionell Verkstad
Produktionsutveckling av Funktionell Verkstad
(Production Development of Functional Workshop)
Marcus Kullerstedt (& Asutay Altay)
Luleå University of Technology
Masters in Mechanical Engineering • October 2016
 Presented in Swedish, this report presents a master thesis project conducted at Siemens Industrial Turbomachinery AB (SIT) in Finspång, Sweden. Due to a strong market and an increased global demand for industrial gas turbines, SIT decided to increase their production capacity. During this process, a bottleneck in the production of burners was found. This Master’s Thesis was created to evaluate possible solutions to this problem.
Presented in Swedish, this report presents a master thesis project conducted at Siemens Industrial Turbomachinery AB (SIT) in Finspång, Sweden. Due to a strong market and an increased global demand for industrial gas turbines, SIT decided to increase their production capacity. During this process, a bottleneck in the production of burners was found. This Master’s Thesis was created to evaluate possible solutions to this problem.
 In this report, the production of burners are evaluated first with a qualitative and quantitative study to gain knowledge of the true capacity. Then, a simulation model of the burner production is built in ExtendSim. The model shows that the capacity can be increased to meet demand without large investments, and also that there is a large potential for improvements, both in production methods and in planning. The use of simulation has made it possible to evaluate the above mentioned dilemmas without affecting daily work and to see the effect that disturbances have on lead time.
In this report, the production of burners are evaluated first with a qualitative and quantitative study to gain knowledge of the true capacity. Then, a simulation model of the burner production is built in ExtendSim. The model shows that the capacity can be increased to meet demand without large investments, and also that there is a large potential for improvements, both in production methods and in planning. The use of simulation has made it possible to evaluate the above mentioned dilemmas without affecting daily work and to see the effect that disturbances have on lead time.
By request from the company, some sensitive content has been placed in a separate appendix, not available to the general public.
Results and Conclusions
From the simulation results, it is possible to ascertain that there is no major restructuring needed to be able to handle the increase in capacity. The employment of additional staff or further training of existing employees might be all that is needed to achieve the best results. Through further smaller investments there is the opportunity to inprove the entire production. The simulation model enables you to investigate in a short period of time and with minimal effort the actions that would result in the greatest increase in productivity, which can then be set in proportion to the cost of implementing each measure. Based on the simulation results, the recommendation is to reduce the batch size from today's mode to achieve a lower lead time and higher flexibility in production, however, this requires development of working methods.
Reliability in Rail Transportation
 Reliability Modelling of ERTMs/ETCS
Reliability Modelling of ERTMs/ETCS
Raja Gopal Kalvakunta
Norwegian University of Science & Technology
MSc. Reliability Availability Maintainability and Safety (RAMS) • June 2017
Abstract
The European railway industry is continuously advancing and in recent years, they have adopted a new system called European Railway Traffic Management System/ European Train Control System (ERTMS/ETCS) for the interoperability of railways among different European nations. Currently, this has been used more extensively for transportation by commuters and for freight. The foremost quality of such transportation system is to operate in a reliable manner and maintain punctuality. In this context, Bane Nor (Norwegian National Rail Administration) is planning to convert the entire conventional signalling system to ERTMS signaling system, as a part of their ERTMS National Implementation project.
ERTMS/ETCS is a complex infrastructure of various systems on trackside, lineside and train onboard and these systems have different sub systems comprising of software, hardware, network and signalling components. Due to its complexity, determining the failures and resolving them is challenging. An existing line operated on ERTMS is taken as case study from Bane NOR for developing a reliability model.
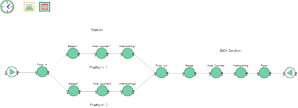 Primarily a reliability block diagram method is used to model the Østfoldbanen Østre Linje (ØØL) ERTMS pilot line as a case study in using the ExtendSim Reliability module incorporating a combination of single station and bidirectional (BiDi) sections, then conducting 1000 simulations to assess ØØL ERTMS infrastructure. It is estimated from the simulation results that this model has the potential to determine the performance of the infrastructure, and it is deduced that predominant infrastructure failures that cause delays are due to partial interlocking fail, maintenance and track fracture, followed by failure of balise, axle counters, and points.
Primarily a reliability block diagram method is used to model the Østfoldbanen Østre Linje (ØØL) ERTMS pilot line as a case study in using the ExtendSim Reliability module incorporating a combination of single station and bidirectional (BiDi) sections, then conducting 1000 simulations to assess ØØL ERTMS infrastructure. It is estimated from the simulation results that this model has the potential to determine the performance of the infrastructure, and it is deduced that predominant infrastructure failures that cause delays are due to partial interlocking fail, maintenance and track fracture, followed by failure of balise, axle counters, and points.
Approach
Though the system is complex, some of the realistic assumptions will be made to design the model considering the vital components of ERTMS. In addition to using the ExtendSim Reliability module, DNV GL also provided their software TRAIL, which is exclusively made for the rail industry and was used to model the entire line section. The approach was to compare all the simulation results i.e. from RelySim, DNV GL, and Bane NOR for identifying the factors that influence the reliability of ERTMS.
Monte Carlo discrete event simulations were implemented using ExtendSim and TRAIL creating virtually real-time railway operations with all the components following their statistical pattern of failure. The failure data and other parameters are taken from the RAM analysis of the existing ERTMS line provided by Bane NOR.
Results and Conclusions
The ExtendSim model created for this thesis, has the capacity to assess the system infrastructure's performance using discrete event simulation to determine the availability of various systems. It was found from ExtendSim that partial interlocking fail, maintenance, and track fracture will occur often and contribute to delays.
Recycling
 Trading and Marketing of Recycled Glass
Trading and Marketing of Recycled Glass
Vera Schmidtmann
University of Cologne
Masters in Operations Research & Decision Support Systems • April 2011
Abstract
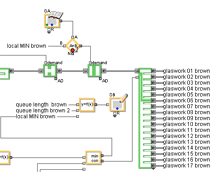 In Germany providers of so-called "dual systems" organize the collection and recycling of waste glass under the well-known license symbol "Der Grüne Punkt" ("The Green Dot").
In Germany providers of so-called "dual systems" organize the collection and recycling of waste glass under the well-known license symbol "Der Grüne Punkt" ("The Green Dot").
Providers of dual systems coordinate which quantities the glass recycling plants obtain from the locally collected glass and which quantities the glass recycling plants deliver to which glassworks. The companies have to consider the transportation and storage costs. The problem is to determine the optimal distribution of the quantities in the network.
For the implementation of the simulation model, the simulation software ExtendSim AT was selected.
Resource Allocation Patterns • Business Process Simulation
 Resource-aware Business Process Simulation: An Approach Based on Workflow Resource Patterns and ExtendSim
Resource-aware Business Process Simulation: An Approach Based on Workflow Resource Patterns and ExtendSim
Nehal Samy Afifi
Cairo University
PhD in Information Systems • April 2018
Abstract
Simulation of business processes is one of the widely-used approaches supporting organization’s decisions and planning changes. One of the limitations of existing process-aware simulation approaches is the poor support for the resource perspective. Without proper modeling of human resource behavior as well as constraints on that behavior, the results of the simulation studies will be incorrect and misleading.
This paper is taking a first step towards a resource-aware business process simulation. We are building on the well-known workflow resource patterns and model them in process simulation models. First contribution is that we refine the relationship among those patterns to modularize their realization in either a simulation or an enactment environment. Second contribution is realization of those patterns in ExtendSim, a general purpose simulation tool. We evaluate our approach on a sample scenario and report the results compared to resource-ignorant approaches.
Approach
The main objective was to specify the missing resources allocation patterns that were ignored by other BPS approaches to come out with correct simulation results based on accurate simulation model reflecting the business process behavior to correctly predict how the real-world processes or systems would operate using specific inputs. Workflow resource patterns were depended on to represent allocation specification.
We have taken a first step towards resource-aware process simulation by modeling workflow resource creation and push patterns in ExtendSim. We have evaluated our approach against other process-specific simulation tools and showed that results are similar for commonly supported scenarios. Moreover, we evaluated different what-if scenarios that were guided by the total number of completed cases in the simulation run.
So far, resources were modeled as passive elements. In the future, we aim at modeling pull workflow patterns in which resources can actively select what work items to execute. Moreover, we aim at supporting complex task lifecycles where a work item can be delegated, canceled, failed etc.
Safety Instrumented Systems & Component Failure
 Safety Instrumented Systems Operated in the Intermediate Demand Mode
Safety Instrumented Systems Operated in the Intermediate Demand Mode
Kristine Tveit
University of Oslo
Master of Science in Modeling & Data Science • December 2015
Abstract
The frequency of demands are crucial when analysing a safety instrumented system (SIS). IEC 61508 distinguishes between low and high demand mode when calculating risk for such a system. In reality there are systems that can not clearly be placed in one of the two modes. These types of systems are called intermediate demand mode systems, which we will analyse in this thesis. Not many published SIS reliability studies focus on the problems related to this borderline. Oliveira [4] predicts somewhat strange behaviour for the hazard rate in the intermediate demand mode, as well as [2] with a focus on the demand duration.
The results from the analyses of a redundant system show that the standard Probability of Failure on Demand (PFD) formulae are usable for very low demand rates, but become increasingly more conservative as one moves into the intermediate mode, while the Probability of Failure per Hour (PFH) is non-conservative. This can cause major consequences for the operator of a safety system in the sense of not obtaining the optimal testing strategy, or even worse encounter a hazard.
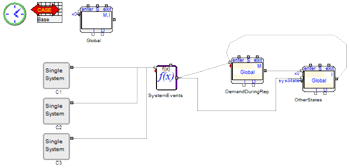 For more complex systems with several components the Markov approach has its limits, choice of distributions and maintenance details are also restricted. Discrete Event simulation can deal with such complex systems, and also the rare event problem that often is a challenge for safety system analysis can be handled satisfactorily.
For more complex systems with several components the Markov approach has its limits, choice of distributions and maintenance details are also restricted. Discrete Event simulation can deal with such complex systems, and also the rare event problem that often is a challenge for safety system analysis can be handled satisfactorily.
By use of Harel Statechart and discrete event Monte Carlo simulations for different safety systems, it is shown that the intermediate demand mode is dependent on the relationship between the proof-tests, demands and repair duration. When a demand rate increases to a significant level, demands can be used as tests. With Harel Statecharts we can calculate realistic models that go beyond what a Markov model is capable of.
Other Publications by this Researcher
S. Eisinger & L.F. Oliveira of DNV GL, Oslo & Rio and K. Tveit & B. Natvig, University of Oslo, Norway. "Safety Instrumented Systems operated in the Intermediate Demand Mode." ESREL Conference, September 8, 2015.
Scheduling Issues Solved Sustainably by Using Energy-Aware Techniques
 Energy-Aware Operations Scheduling
Energy-Aware Operations Scheduling
Ali Mohamed Fathy, Mostafa Ayman Nabhan, Huda Ahmed Afifi, & Pola Adel Mahrous
Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport • College of Engineering and Technology Industrial and Management Engineering
B. Sc. Final Year Project • September 2021
Abstract
Recently, the need for sustainable manufacturing has been ever-growing and crucial to help sustain the dying resources that earth has provided human beings with, which leaves us with a mission to help save these resources by finding new ways to minimize the use of them. Out of the three main sustainability pillars, social, environmental and economic pillars, the focus in the industrial field is now shifting towards the environmental pillar and especially the energy aspect. Recent research propose different methods and techniques to help reduce the energy consumption on production lines through different strategies. Operations scheduling and sequencing is an important process in any industrial facility, where the utilization of the resources is one of the main objectives. Integrating the concepts of operations scheduling with the sustainability aspect yielded very promising results recently, where optimization models and simulation models where applied to solve the scheduling problem in an energy-aware manner. The focus of this project is to present the recent work that has been done on this topic, and study the concepts used in these papers. A simulation-based approach is proposed and tested on a real-life case study, applying operation scheduling techniques and energy-saving methods.
Approach
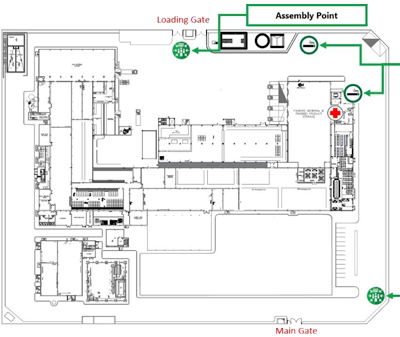 Initially, value stream maps and process flow charts were acquired from the manufacturing process of a chewing gum company. These data were used to create an ExtendSim simulation model where the current state of the production line was studied and analyzed, and the results verified and validated. The next step was trying different scenarios that could minimize the energy consumption on the production line while maintaining current KPIs. Multiple scenarios were run and compared to the original system with the best performing scenario being suggested. The focus of the project was to optimize changeover schedules while minimizing the number of stops needed on the machines. Another strategy tested varying machine speeds and studying the effects of these changes on the throughput and the energy consumptions on each machine.
Initially, value stream maps and process flow charts were acquired from the manufacturing process of a chewing gum company. These data were used to create an ExtendSim simulation model where the current state of the production line was studied and analyzed, and the results verified and validated. The next step was trying different scenarios that could minimize the energy consumption on the production line while maintaining current KPIs. Multiple scenarios were run and compared to the original system with the best performing scenario being suggested. The focus of the project was to optimize changeover schedules while minimizing the number of stops needed on the machines. Another strategy tested varying machine speeds and studying the effects of these changes on the throughput and the energy consumptions on each machine.
ExtendSim was used to create a discrete event simulation model that represents the production line. The main phase of the project was to optimize the machine speeds and changeover schedules to study results of different scenarios while maintaining an acceptable mean cycle time, throughput rate and average waiting times, and considering different constraints like due dates and demand plans. Multiple scenarios were tested in ExtendSim utilizing the Scenario Manager and Optimizer blocks to reach the most suitable and preferably optimal scenario for the production line to suggested to the manufacturing company. The Equation block was used to manage condition codes to help create a model that functions as close as possible to the real life production line. ExtendSim databases manage the changeover schedules between the different product types and the setup time needed between the product matrix.
Results and Conclusions
Integrating sustainability aspects with operational production scheduling proved to yield significant results. Minimizing energy costs just by scheduling the operations on a production is significant on an environmental level, even more than on economical levels. Finding a suitable changeover schedule can make huge differences on the production level, whether minimizing energy costs, minimizing the number of stops and increasing the production line productivity. Going with the simulation approach lead to the testing of many scenarios in a very short time period, giving more time for result analysis and finding ways to reduce the energy consumption even more, whether by finding a more suitable changeover schedules, or discovering bottlenecks that would not have been discovered by other solution techniques. The speed-scaling strategy proved to have a far more important role than just reducing the energy consumptions on machines by slowing them. Utilizations of production lines can be increased if the position of bottlenecks can be identified and the machine speeds are increased slightly.
Most objectives that were set before the start of the project were achieved within the timescale. Implementation of the project and testing more strategies could not be completed within the timescale due to the COVID-19 crisis, which made visits and more in depth data collection not possible. Further research can be done where different energy-saving strategies can be used and discover the effect they have on the energy consumption and productivity of a production line. It is recommended that more accurate data regarding the effect of different machine speeds on their energy consumption can be collected to measure the full extent of changing machine speeds and how it effects the performance measures of the production line.
Service Systems • Queue Analysis
 Managing Service Systems with an Offline Waiting Option and Customer Abandonment
Managing Service Systems with an Offline Waiting Option and Customer Abandonment
Vasiliki Kostami (with Sriram Dasu & Amy Ward)
University of Southern California
PhD in Operations Management • December 2008
Many service providers offer customers the choice of either waiting in a line, or going offline and returning at a dynamically determined future time. The best known example is the FASTPASS® system at Disneyland. To operate such a system, the service provider must first make an up front decision on how to allocate service capacity between the two lines. Then, during system operation, he must dynamically provide estimates of the waiting times at both lines to each arriving customer. The estimation of offline waiting times is complicated by the fact that some offline customers do not return for service at their appointed time.
"Managing Service Systems with an Offline Waiting Option and Customer Abandonment" shows that when demand is large and service is fast, for any fixed capacity allocation decision, the two-dimensional process tracking the number of customers waiting inline and offline collapses to one dimension, and characterize the one-dimensional limit process as a reflected diffusion with linear drift. Next, using the one-dimensional limit process to develop approximations for the steady-state distribution of the number of customers waiting inline and offline, the steady-state probability of abandonment from the offline queue, and to dynamically estimate inline and offline waits for each arriving customer is used. The paper concludes by considering a cost model that optimizes the up front capacity allocation decision.
Supply Chain • Channel Sourcing
 Impact of Unauthorized Distributors on the Supply Chain and Financial Performance of Companies
Impact of Unauthorized Distributors on the Supply Chain and Financial Performance of Companies
Youness Eaidgah
Kungliga Tekniska Högskolan
Master of Science in Production Engineering & Management • August 2012
Global supply chains, shorter product life cycles, and technological innovation have made supply chain management a critical issue for a firm’s success. By improving service and reducing costs, efficient supply chain management brings companies competitive advantage and helps them to outperform their competitors. Due to tight supply or unfavorable conditions, an Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) might occasionally find itself in a situation where it is not able or willing to source its required raw material from an authorized channel. In this case, OEM options narrow down to waiting until the item become available in the authorized channel (backlogging its customer orders), sourcing from unauthorized channel, or cancelling customer orders. Each one of these scenarios causes particular consequences.
 The main objective of this study is to clarify the consequences of sourcing from unauthorized distributors on supply chain performance and its financial performance of the OEM. The study is composed of a qualitative phase and a quantitative phase. During each phase, a proper set of supply chain metrics and financial measures are employed to understand the effects of sourcing from unauthorized distributors and counterfeits parts. In both phases, a SCOR model is used as a reference for supply chain metrics as well as to understand the supply chain processes.
The main objective of this study is to clarify the consequences of sourcing from unauthorized distributors on supply chain performance and its financial performance of the OEM. The study is composed of a qualitative phase and a quantitative phase. During each phase, a proper set of supply chain metrics and financial measures are employed to understand the effects of sourcing from unauthorized distributors and counterfeits parts. In both phases, a SCOR model is used as a reference for supply chain metrics as well as to understand the supply chain processes.
Based on the study results, there is obviously a trade-off involved in sourcing from an unauthorized channel. It may help the OEM in some respects; however, it may pose a risk to the OEM performance at the same time. The particular circumstance of each business is a key factor to determine the effects. Among the factors studied, raw material quality, sourcing volume, and accusation price are the most important ones respectively. The most influential factor is raw material quality and it mostly outweighs the effect of the unauthorized distributors’ lower prices. It implies that lower prices should not be the sole incentive to source from unauthorized channel. Concerning all factors is a must. In the case that the OEM decides to source from an unauthorized channel, proper risk mitigation methods should be employed to reduce the risk of receiving low quality articles.
Approach
During the research period, the interaction between supply chain performance and financial performance in the presence of counterfeit electronic parts was researched. The study was divided into two phases, qualitative study and quantitative study. Through the qualitative study, after a comprehensive literature review, the potential interaction between supply chain non-cost performance measures and financial ratios was examined. During the quantitative phase, a combination of simulation, Design of Experiments (DOE), and regression analysis was used to assess the behavior of parameters.
Results and Conclusions
The quantitative phase of this study was based on a generic supply chain and a two level design of experiment. While this is a proper setting to screen out insignificant factors and to understand the general behavior of parameters, it is not an adequate model to quantify the interactions. A more elaborated model and some case studies are required in this regard. Formulating the interactions between parameters, valuating the quality threshold, and a wider clarification of financial impacts of sourcing decisions could be the next step of this study.
Supply Chain • Perishable and Substitutable Products
 Replenishment Policy for Perishable and Substitutable Products at Suppliers and Retailers: A Multi-Criteria Approach
Replenishment Policy for Perishable and Substitutable Products at Suppliers and Retailers: A Multi-Criteria Approach
Linh Nguyen Khanh Duong
Auckland University of Technology
Doctor of Philosophy in Supply Chain Management • February 19, 2018
Abstract
 Defining replenishment policies for perishable products is an important activity, particularly where suppliers have a range of products. As product ranges increase, consumers can substitute products if their preferred product is out of stock. Such substitution considered simultaneously as perishability makes it difficult to achieve balanced results over different departments/companies in the face of fluctuating demand. Given these circumstances, a financially calculated replenishment policy makes communicating the impact of operational changes difficult. In contrast, non-financial measures improve the communication between departments and staff (e.g., between warehousing, procurement, and sales), and allows them to set operational targets from broad corporate strategies.
Defining replenishment policies for perishable products is an important activity, particularly where suppliers have a range of products. As product ranges increase, consumers can substitute products if their preferred product is out of stock. Such substitution considered simultaneously as perishability makes it difficult to achieve balanced results over different departments/companies in the face of fluctuating demand. Given these circumstances, a financially calculated replenishment policy makes communicating the impact of operational changes difficult. In contrast, non-financial measures improve the communication between departments and staff (e.g., between warehousing, procurement, and sales), and allows them to set operational targets from broad corporate strategies.
This study contributes to inventory management theory by being the first research to develop a non-financial framework and demonstrate that it is comparability to financial approaches for perishable and substitutable inventory. For managers, this study contributes by providing a framework (based on non-financial measures) to develop or modify replenishment policies to balance service level/cost in contexts with perishable and substitutable products. The framework is particularly relevant for suppliers, as they are more impacted by fluctuating demand. The non-financial approach also enables managers to evaluate the effectiveness of other supplementary techniques (e.g., forecasting techniques) in the inventory management when making a business case.
Simulation Approach
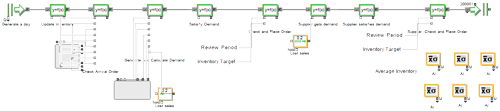
A discrete-event simulation model was developed to enable a comparison of performance of multiple systems. Using sensitivity analysis and other advanced search techniques in simulation, feasible solutions were evaluated to obtain optimal results. This type of inventory model must account for a range of assumptions that closely mirror the situations found in real inventory systems. These include:
- Shelf-life: products were assumed to have a constant shelf-life.
- Demand: to use a simulation - optimization approach, using a discrete distribution is preferred.
- The profit margin: it was assumed that the profit margin for each product is the same although the price and unit cost can vary for each product.
- The replenishment lead time was deterministic.
- All products arrived into the system as 'new' products.
- Substitution was considered to be consumer-driven. For example, the customer considered to buy an apple with first preference being A brand, the second preference B brand. The customer will look for fresh A brand first. If there is no fresh A brand, the customer will choose among four alternatives:
- Substitute with older A brand product if it was available.
- Substitute with fresh B brand product if it was available.
- Substitute with old B brand if no A brand is available and no fresh B brand was available.
- Decide not to buy either A or B brand product
Results and Conclusions
The results showed that the consumer demand, product lifetime, and substitution inputs to the model have large effects on retailers’ and supplier performance; however, only the interaction between consumer demand and product lifetime had a similarly large effect on firms’ performance. Suppliers are more greatly affected by the bullwhip effect in the model; in contrast, the effects on the retailers is smaller. Moreover, this research also shows that, in the studied context, the most favourable replenishment policy is stable under changes in the weights of performance measures.
Other Publications by this Researcher
Duong, L. N. K., Wood, L. C., & Wang, X. (2016). Review of RFID Applications in Perishable Inventory Management. In B. Christiansen (Ed.), Handbook of Research on Global Supply Chain Management (pp. 139-146). Hershey, PA: Business Science Reference. doi:10.4018/978-1-4666-9639-6.ch008.
Duong, L. N. K., Wood, L. C., & Wang, W. Y. C. (2015). A Multi-criteria Inventory Management System for Perishable & Substitutable Products. Procedia Manufacturing, 2(February), 66–76. doi:10.1016/j.promfg.2015.07.012.
Duong, L. N. K., Wood, L. C., & Wang, W. (2015). A review and reflection on inventory management of perishable products in a single-echelon model. International Journal of Operational Research, June 2015.
Duong, N. K. L. & Wood, L. C. (2015). Simulation to improve management of perishable and substitutable inventory. In Encyclopedia of Information Science and Technology, Edition: 3rd, Chapter: 84, Publisher: Information Science Reference, Editors: M. Khosrow-Pour, pp.915-922.
Sustainability Science
 Ensuring Water Security for the Sustainability of the Hani Rice Terraces, China Against Climate and Land Use Changes
Ensuring Water Security for the Sustainability of the Hani Rice Terraces, China Against Climate and Land Use Changes
Archana Jayaraman (with Dr. Srikantha Herath & Johanna Diwa)
United Nations University
Masters in Sustainability Science • February 2017
Project details
 Building upon a 2013 report on developing ecosystem-based adaptation strategies for enhancing the resilience of rice terrace farming systems against climate change for the Asia-Pacific Network for Global Change Research, Archana Jayaraman took the project one step further.
Building upon a 2013 report on developing ecosystem-based adaptation strategies for enhancing the resilience of rice terrace farming systems against climate change for the Asia-Pacific Network for Global Change Research, Archana Jayaraman took the project one step further.
The hydrological system of the Hani Rice Terraces in Yunnan, China was modelled using the Similar Hydrologic Element Response (SHER) model in ExtendSim. Two models were built, for the upstream and downstream catchments and were calibrated using global datasets. Further analysis was done on the behaviour of the model under future climate scenarios using the RCP predicted data.
Abstract
 This study aims to assess the hydrological response of the selected study sites in the Hani Rice Terrace to climate change. Subsequently, it sets a process for analyzing a complex, interconnected hydrological system with varying topography and containing different landscape elements across different reaches for enhancing livelihoods of terrace communities. In the current analysis, instances of scarcity and periods of concentrated availability have been noticed, both in the upstream and the downstream reaches, under historical and future rainfall scenarios and demand changes. Reconciling water availability with equitable access has been identified as the most important issue that needs policy formulation and institutional arrangements. In this research, water scarcity index as a tool is used to identify and understand threats to water security and is found to be an appropriate way of looking at overall changes in demand and supply. The analysis is conducted with available spatial data derived from satellite and global data sets complimented with field surveys, and estimates are expected to be representative. It is seen that the water scarcity index can also be used to identify periods in which action is required and show if interventions can really help solve a given problem in a simple manner.
This study aims to assess the hydrological response of the selected study sites in the Hani Rice Terrace to climate change. Subsequently, it sets a process for analyzing a complex, interconnected hydrological system with varying topography and containing different landscape elements across different reaches for enhancing livelihoods of terrace communities. In the current analysis, instances of scarcity and periods of concentrated availability have been noticed, both in the upstream and the downstream reaches, under historical and future rainfall scenarios and demand changes. Reconciling water availability with equitable access has been identified as the most important issue that needs policy formulation and institutional arrangements. In this research, water scarcity index as a tool is used to identify and understand threats to water security and is found to be an appropriate way of looking at overall changes in demand and supply. The analysis is conducted with available spatial data derived from satellite and global data sets complimented with field surveys, and estimates are expected to be representative. It is seen that the water scarcity index can also be used to identify periods in which action is required and show if interventions can really help solve a given problem in a simple manner.
Results and Conclusions
This research analyzed different components of the hydrological system in the area and clarified the contribution of the surface and groundwater flow in the area. The need to assess both, while also looking at the total water cycle, for estimating the availability of water in the system and the future changes, was identified as a key parameter for ensuring water security. Water scarcity was estimated in terms of the balance between availability and use, and it was found that there were periods of water scarcity in the area, with differences in the upstream and downstream reaches of the system. It has been shown that solving development challenges requires a multi-stakeholder strategy as the system is deeply intertwined with the social setup in the area, and the use of tools such as the water scarcity index can be done to aid effective problem identification and decision making regarding the timing and effects of interventions on the ground.
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their thanks to the Asia-Pacific Network for Global Change Research (ARCP2011-13NMY-Herath) for supporting the field research. The support of the people of Hani rice terraces who helped in the field work is gratefully acknowledged.
Transportation • Construction Projects
 Conceptual Methodology for Managing Transportation Construction Projects Through the use of Buffering Strategies
Conceptual Methodology for Managing Transportation Construction Projects Through the use of Buffering Strategies
Eric Forcael ( with Vicente González, PhD; Ralph Ellis, PhD; & Francisco Orozco, PhD)
University of Florida
PhD in Civil & Coastal Engineering • August 2011
Project presented at
 Ninth LACCEI Latin American and Caribbean Conference (LACCEI 2011), Engineering for a Smart Planet, Innovation, Information Technology and Computational Tools for Sustainable Development, August 3-5, 2011, Medellín, Colombia.
Ninth LACCEI Latin American and Caribbean Conference (LACCEI 2011), Engineering for a Smart Planet, Innovation, Information Technology and Computational Tools for Sustainable Development, August 3-5, 2011, Medellín, Colombia.
Abstract
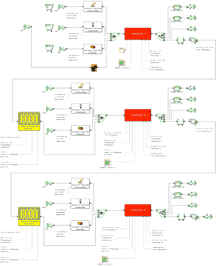 Uncertainty is an inherent part of production systems. In construction processes, production variability emerges as one of the most typical representation of uncertainty. Negative variability impacts in construction demands effective solutions to mitigate its effects on the accomplishment of projects. The incorporation of buffers constitutes powerful tools to resolve uncertainty problems in construction processes and to optimize the construction operations sequencing. Despite the fact that buffering strategies have been implemented in several types of construction projects, there is limited evidence of specific applications of these strategies to highway projects. Based on discrete event simulation modeling, a conceptual methodology of buffering strategies applied to transportation projects is presented.
Uncertainty is an inherent part of production systems. In construction processes, production variability emerges as one of the most typical representation of uncertainty. Negative variability impacts in construction demands effective solutions to mitigate its effects on the accomplishment of projects. The incorporation of buffers constitutes powerful tools to resolve uncertainty problems in construction processes and to optimize the construction operations sequencing. Despite the fact that buffering strategies have been implemented in several types of construction projects, there is limited evidence of specific applications of these strategies to highway projects. Based on discrete event simulation modeling, a conceptual methodology of buffering strategies applied to transportation projects is presented.
After an exhaustive literature review, the most relevant buffers in transportation construction projects are presented, followed by conceptually modeling a typical construction process within highway projects. Through this methodology, the authors present an iterative process which allows decision-makers to properly select buffers to be considered when modeling construction processes in transportation construction projects.
Approach
Specifically, this research searched to study and analyze different types of buffers in order to figure out which are more relevant in road projects. Then, the buffers, which were chosen in the first part of this research, were modeled with ExtendSim and, subsequently, validated through a case of study.
Results and Conclusions
This paper was focused on proposing and testing a simple graphical approach based on simulation techniques and buffering strategies applied to transportation construction projects and, more generally, proposing a conceptual methodology to build simulation-based models that help deal with the negative impact of variability on this type of projects.
This conceptual methodology allows the researcher to develop a simulation-based model for any type of transportation construction project, with the final and most appreciated objective of utilizing the outputs of the model as a tool for decision-makers. This methodology permits to select the appropriate activities to be included in the model, to select the buffers, to compare the outputs given by the model with actual data, to determine whether the buffers are statistically significant (ANOVA, MANOVA) and, if not, to loop back to previous steps to feedback the model with the relevant buffers found, finishing the process with the utilization of the outputs information in order to make better decisions.
Transportation • Traffic Signal Timing
 Optimization of Traffic Signal Timings Using Genetic Algorithm, Simulation, and FPGA Control
Optimization of Traffic Signal Timings Using Genetic Algorithm, Simulation, and FPGA Control
Ahmed Aziz Ezzat (with Julia El Zoghby, Mohamed El Ahmar, Nermine Hany, Azmy Mehelba, & Ezz Abou Emira)
Arab Academy for Science, Technology, and Maritime Transport
Bachelor of Science for the Department of Industrial & Management Engineering • July 2013
Abstract
Traffic congestion is a major problem in vastly populated cities. This project focuses on the traffic crisis seen in Alexandria, which occurs due to the absence of a reliable control strategy that regulates the traffic signal lights. As a result, a substantial growth of the vehicles' queue lengths and delays emerges. The main aim of this project is to minimize the traffic congestion for a traffic control system, considering the traffic signal timings rendered to a number of control points in specified intersections. In order to satisfy this goal, a set of objectives to be carried out through the project are established.
 The main objectives include developing an analytical model representing the traffic system and proposing a solution approach using the Genetic Algorithm technique. Furthermore, developing a simulation model for the problem in order to replicate and analyse the performance of the real system, as well as suggesting better scenarios to improve the overall system efficiency. Furthermore, a simulation model is developed to represent a smart traffic control system, and evaluate its correspondent performance compared to the current situation. In addition, employing optimization using simulation methodology to reach the best possible traffic light timings, and last but not least, studying the possibility of applying FPGA's for the control of traffic systems.
The main objectives include developing an analytical model representing the traffic system and proposing a solution approach using the Genetic Algorithm technique. Furthermore, developing a simulation model for the problem in order to replicate and analyse the performance of the real system, as well as suggesting better scenarios to improve the overall system efficiency. Furthermore, a simulation model is developed to represent a smart traffic control system, and evaluate its correspondent performance compared to the current situation. In addition, employing optimization using simulation methodology to reach the best possible traffic light timings, and last but not least, studying the possibility of applying FPGA's for the control of traffic systems.
The report focuses on generating different scenarios and various solutions through experimenting with the developed models in order to optimize the traffic signal timings. Comparisons are held between different approaches and methodologies to achieve the best possible performance and cut off the traffic congestion problem from its root causes.
Uncertainty in Software Engineering
 Studying the Impact of Uncertainty in Operational Release Planning - An Integrated Method and its Initial Evaluation
Studying the Impact of Uncertainty in Operational Release Planning - An Integrated Method and its Initial Evaluation
Ahmed Al-Emran (with Puneet Kapur, Dietmar Pfahl, & Guenther Ruhe)
University of Calgary
PhD in Software Engineering • July 2009
Project presented at
 International Conference on Software Process (ICSP) 2010
International Conference on Software Process (ICSP) 2010
July 2010 • Paderborn, Germany
Journal article published in
 Information and Software Technology
Information and Software Technology
Volume 52, Issue 4, April 2010
pages 446-461
Abstract
Context
Uncertainty is an unavoidable issue in software engineering and an important area of investigation. This paper studies the impact of uncertainty on total duration (i.e., make-span) for implementing all features in operational release planning.
Objective
The uncertainty factors under investigation are:
- the number of new features arriving during release construction.
- the estimated effort needed to implement features.
- the availability of developers.
- the productivity of developers.
Approach
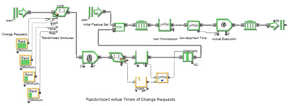 An integrated method is presented combining Monte-Carlo simulation (to model uncertainty in the operational release planning (ORP) process) with process simulation (to model the ORP process steps and their dependencies as well as an associated optimization heuristic representing an organization-specific staffing policy for make-span minimization). The method allows for evaluating the impact of uncertainty on make-span. The impact of uncertainty factors both in isolation and in combination are studied in three different pessimism levels through comparison with a baseline plan. Initial evaluation of the method is done by an explorative case study at Chartwell Technology Inc. to demonstrate its applicability and its usefulness.
An integrated method is presented combining Monte-Carlo simulation (to model uncertainty in the operational release planning (ORP) process) with process simulation (to model the ORP process steps and their dependencies as well as an associated optimization heuristic representing an organization-specific staffing policy for make-span minimization). The method allows for evaluating the impact of uncertainty on make-span. The impact of uncertainty factors both in isolation and in combination are studied in three different pessimism levels through comparison with a baseline plan. Initial evaluation of the method is done by an explorative case study at Chartwell Technology Inc. to demonstrate its applicability and its usefulness.
Results and Conclusions
Results
The impact of uncertainty on release make-span increases – both in terms of magnitude and variance – with an increase of pessimism level as well as with an increase of the number of uncertainty factors. Among the four uncertainty factors, we found that the strongest impact stems from the number of new features arriving during release construction. We have also demonstrated that for any combination of uncertainty factors their combined (i.e., simultaneous) impact is bigger than the addition of their individual impacts.
Conclusion
The added value of the presented method is that managers are able to study the impact of uncertainty on existing (i.e., baseline) operational release plans pro-actively.
Other Publications by this Researcher
Journal Articles
[J1] Ahmed Al-Emran, Dietmar Pfahl, Günther Ruhe: A Method for Re-Planning of Software Releases using Discrete-Event Simulation. Accepted in Software Process Improvement and Practice under special issue “ICSP 2007”.
[J2] Ahmed Al-Emran, Dietmar Pfahl: Performing Operational Release Planning, Re-planning and Risk Analysis using a System Dynamics Simulation Model. Accepted in Software Process Improvement and Practice under special issue “PROFES 2007”.
[J3] Dietmar Pfahl, Ahmed Al-Emran, Günther Ruhe: A System Dynamics Model for Analyzing the Stability of Software Release Plans. Published in Software Process Improvement and Practice 12 (2007) 5, 475-490.
[J4] Jingzhou Li, Günther Ruhe, Ahmed Al-Emran, Michael M. Richter: A Flexible Method for Software Effort Estimation by Analogy. Empirical Software Engineering 12 (2007) 1, 65-106.
Conference Papers
[C1] Anas Jadallah, Ahmed Al-Emran, Mahmoud Moussavi, Günther Ruhe: The How? When? and What? for the Process of Re-Planning for Product Releases. Accepted in International Conference on Software Process (ICSP) 2009.
[C2] Ahmed Al-Emran, Puneet Kapur, Dietmar Pfahl, Günther Ruhe: Simulating Worst Case Scenarios and Analyzing their Combined Effect in Operational Release Planning. Accepted in International Conference on Software Process (ICSP) 2008.
[C3] Ahmed Al-Emran, Keyvan Khosrovian, Dietmar Pfahl, Günther Ruhe: Simulation-Based Uncertainty Analysis for Planning Parameters in Operational Product Management. Published in Proceedings of the 10th Int. Conference on Integrated Design and Process Technology (IDPT) 2007. Antalya, Turkey, June 3-8, 2007, 191-201.
[C4] Ahmed Al-Emran, Dietmar Pfahl: Operational Planning, Re-Planning and Risk Analysis for Software Releases. Published in International Product Focused Software Development and Process Improvement (PROFES) Conference 2007 - Proceedings. Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2007, 315–329 (Lecture Notes in Computer Science 4589).
[C5] Ahmed Al-Emran, Dietmar Pfahl, Günther Ruhe: DynaReP: A Discrete Event Simulation Model for Re-Planning of Software Releases. Published in International Conference on Software Process (ICSP) 2007 - Proceedings. Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2007, 246-258 (Lecture Notes in Computer Science 4470).
[C6] Dietmar Pfahl, Ahmed Al-Emran, Günther Ruhe: Simulation-Based Stability Analysis for Software Release Plans. Published in International Software Process Workshop and International Workshop on Software Process Simulation and Modeling, SPW/ProSim 2006 - Proceedings. Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2006, 262-273 (Lecture Notes in Computer Science 3966).
Value Stream Mapping • Complex Production Environments
 A Simulation-Enhanced Value Stream Mapping Approach for Optimisation of Complex Production Environments
A Simulation-Enhanced Value Stream Mapping Approach for Optimisation of Complex Production Environments
David Schmidtke (with U. Heiser & O. Hinrichsen)
Technical University of Munich
PhD in Chemical Engineering • June 2014
Project presented in
 International Journal of Production Research
International Journal of Production Research
May 16, 2014
Abstract
Value stream mapping (VSM) is a widely adopted method for transformation of production environments into a lean operational state. The straightforwardness as well as the completeness, with which processes are analysed and optimised, are key to the success of the method originating from the automotive industry. However, these attributes of the ‘paper and pencil’ approach result in limitations when applying VSM in complex production environments. This research paper targets to overcome these limitations, specifically in production environments involving significant demand variability, complex routing and cost factors which potentially increase with lean implementation. For this purpose, an enhanced VSM method is developed, which utilises discrete event simulation (DES). The method features a feasibility and trade-off analysis which is incorporated into the VSM procedure. A case study covering a process of exhaust gas purification catalyst production is then conducted to test the newly developed method. The VSM project yields a shop floor lead time reduction from 11.4 to 1.4 d. The additional DES feasibility and trade-off analysis determines customer demand fulfilment and quantifies the monetary benefit of the future state. In that way, potential iterative implementation which is inherently oppositional to the lean philosophy is avoided.
ExtendSim use
After successful utilization of discrete event simulation as a decision-making tool in a VSM project for optimization of a discrete part chemical model process, the procedure was transferred to chemical bulk products. Initially, ExtendSim discrete rate simulation was adapted to the requirements of a two-component chemical process, in which separation takes place. For this purpose, a parallel process for the second component (diluted salt) is added to the model of the overall volume. Both components are linked by through mass balance.
The overall model is divided into two areas:
I. Flow area
Flow between tanks and vessels takes place at constant salt concentration. Therefore, the salt rate is linked to the regulated volume rate as well as the concentration inside the upstream tank. Simple flow area connections can be analytically solved with linear differential equations. Concurrence with the analytical solution validates the modeling approach.
II. Separation area
Wherever separation takes place, two streams with changed salt concentrations evolve from one feed stream. Distribution of both, volume and concentration of the product stream depend on feed parameters (volume flow and concentration) as well as process parameters (pressure, temperature, etc.). For separation operations, diverge blocks are utilized with distribution ratios calculated from empirical multiple non-linear regression equations. Separation areas can be validated against real-life separators (reverse osmosis units). The accuracy depends on the exactness of the regression equations.
Results of using simulation for VSM
As the static and linear method of VSM has several disadvantages when complex production processes are covered, an integrated VSM/discrete event simulation (DES) procedure has been elaborated. The extended VSM method comprises DES feasibility and trade off analysis prior to implementation of the proposed optimization. When applied thoroughly, the procedure can help to avoid costly iterative implementation by answering the following questions beforehand:
- Are we able to fulfill the customer demand with the proposed VSM future state?
- Is the proposed future state beneficial when all conflicting cost factors are considered?
Furthermore, feasibility and trade off analysis can be a valuable tool for convincing the management of process changes elaborated in a VSM project.
Value Stream Mapping
 Component Based Modeling and Simulation of Value Stream Mapping for Lean Production Systems
Component Based Modeling and Simulation of Value Stream Mapping for Lean Production Systems
Mohamed A. Shararah (in conjunction with Khaled S. El-Kilany & Aziz E. El-Sayed
Arab Academy for Science and Technology
Masters • January 2010
Project presented at
 IIE Lean & Six Sigma Conference
IIE Lean & Six Sigma Conference
Lean & Six Sigma Conference 2011
In addition to the paper's presentation, Mr. Shararah's modeling of value stream mapping concept was recognized in the conference's keynote speach by Tim Copes, the Vice President of Manufacturing and Quality for Boeing commercial airplanes due to its unique application.
Abstract
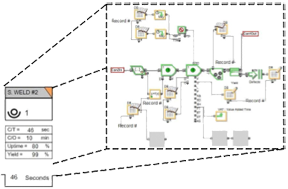 Value Stream Mapping is an important tool in the implementation of lean manufacturing. It identifies the waste in the system, paving the way for a successful lean implementation. VSM is a paper and pencil tool that captures the state of the system at the state it was drawn. Arab Academy modelSimulation can be combined with value stream mapping to give it power and flexibility in order to dynamically capture the state of the system. Component-based modeling divides a simulation model into a number of smaller simulation models each encapsulated in a component resulting in a set of simulation building blocks. These blocks can be used for the purpose of developing value stream maps as they are designed to be generic, reusable, and appear exactly like the traditional VSM icons. This paper introduces the Value Stream Map Simulator using ExtendSim (VSMSx) as a powerful tool designed to facilitate the implementation of lean manufacturing by simulating the value stream map. Compared to traditional value stream mapping, this tool outputs more quantitative information about the system under study and various scenarios allowing for better decision making, thus paving the way for successful lean implementation.
Value Stream Mapping is an important tool in the implementation of lean manufacturing. It identifies the waste in the system, paving the way for a successful lean implementation. VSM is a paper and pencil tool that captures the state of the system at the state it was drawn. Arab Academy modelSimulation can be combined with value stream mapping to give it power and flexibility in order to dynamically capture the state of the system. Component-based modeling divides a simulation model into a number of smaller simulation models each encapsulated in a component resulting in a set of simulation building blocks. These blocks can be used for the purpose of developing value stream maps as they are designed to be generic, reusable, and appear exactly like the traditional VSM icons. This paper introduces the Value Stream Map Simulator using ExtendSim (VSMSx) as a powerful tool designed to facilitate the implementation of lean manufacturing by simulating the value stream map. Compared to traditional value stream mapping, this tool outputs more quantitative information about the system under study and various scenarios allowing for better decision making, thus paving the way for successful lean implementation.
Results and Conclusions
This work presented the combining of value stream mapping and simulation, and how such a combination gave much power and strength to both tools. Simulation added another dimension to VSM which is time, and VSM showed the importance of simulation in modeling production systems.
Using simulation building blocks to model VSM icons gives great flexibility and power to the simulation model. Simulation itself gives another dimension to the VSM which is time, thus making it easy to know the state of the system under different circumstances allowing for better decision making.
Experimenting with a VSMSx model will give information about the system that can be very useful. As when doing a more standard simulation analysis it gives a very good overview of the interaction of the products with each other in the system over time. It also gives some additional information and possibilities. The results can give information on how differences in lead times appear and how lead times relate to value adding times. Experiments can easily be done varying setup times and even some cycle times to see what effects that has on inventory. Also buffer sizes and batch sizes can be altered to see how it affects the system. Another example is the visualization of which machines will give you the best and fastest effect when initiating Single minute exchange of dies (SMED) work. The possibilities are many with VSMSx paving the way towards better lean understanding by decision takers and faster lean implementation.
Water Storage Management • Remotely-Controlled Siphon System
 Operational Reliability Assessment of a Remotely-controlled Siphon System for Draining Shallow Storage Ponds
Operational Reliability Assessment of a Remotely-controlled Siphon System for Draining Shallow Storage Ponds
Linlong Bian
Florida International University
PhD in Civil and Environmental Engineering • June 2021
Additional authors from Florida International University: Vivek Verma, Aditia Rojiali, Sumit R. Zanje, Dogukan Ozecik, and Arturo S. Leon
Abstract
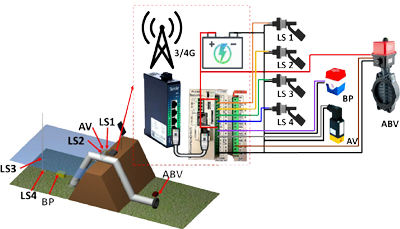 This paper presents the operational reliability assessment of a remotely controlled siphon system. The siphon system consists of water level switches, air vents, bilge pumps, etc. In this study, the reliability block diagram (RBD) model built in the ExtendSim software is applied to assess the operational reliability of a remotely-controlled siphon system. The Monte-Carlo simulation results from the RBD model demonstrate that the operational availability of the non-repairable siphon system can be enhanced from 0.683 to 0.855 within a 1-year life cycle by increasing the redundancy for the vulnerable components, such as the water level switch and the air vent. The value can increase to 0.999 when adopting an on-site maintenance strategy. Based on the analysis of multiple scenarios and maintenance strategies, a suitable architecture of the siphon system is proposed herein.
This paper presents the operational reliability assessment of a remotely controlled siphon system. The siphon system consists of water level switches, air vents, bilge pumps, etc. In this study, the reliability block diagram (RBD) model built in the ExtendSim software is applied to assess the operational reliability of a remotely-controlled siphon system. The Monte-Carlo simulation results from the RBD model demonstrate that the operational availability of the non-repairable siphon system can be enhanced from 0.683 to 0.855 within a 1-year life cycle by increasing the redundancy for the vulnerable components, such as the water level switch and the air vent. The value can increase to 0.999 when adopting an on-site maintenance strategy. Based on the analysis of multiple scenarios and maintenance strategies, a suitable architecture of the siphon system is proposed herein.
Approach
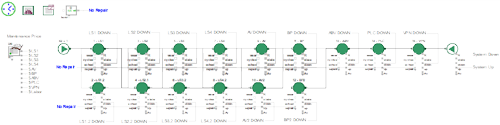 Many methods have been developed to analyze the reliability of a system and each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Traditional approaches, such as the Markov model and Petri nets (PNs), are based on an analytic solution. These approaches need stringent assumptions about the system, such as the lifetime distribution of the components in the system has to obey an exponential distribution and the failure probability has to be independent for all the components. However, in reality many systems can hardly meet these strict conditions. Therefore, the scope of the above analytic approaches is limited in the case of complex systems since the model is hard to obtain directly from the specifications or descriptions of a system. Such inconvenience led to the development of the Reliability Block Diagram (RBD), Fault Trees (FTs), and Reliability Graphs (RGs), which are more user-friendly.
Many methods have been developed to analyze the reliability of a system and each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Traditional approaches, such as the Markov model and Petri nets (PNs), are based on an analytic solution. These approaches need stringent assumptions about the system, such as the lifetime distribution of the components in the system has to obey an exponential distribution and the failure probability has to be independent for all the components. However, in reality many systems can hardly meet these strict conditions. Therefore, the scope of the above analytic approaches is limited in the case of complex systems since the model is hard to obtain directly from the specifications or descriptions of a system. Such inconvenience led to the development of the Reliability Block Diagram (RBD), Fault Trees (FTs), and Reliability Graphs (RGs), which are more user-friendly.
RBD as an efficient tool has been widely used in reliability engineering for many years. When evaluating the operational reliability of a complex system, the significant advantage of RBD is that it describes a system, graphically. All the components in the system can be connected by graphic blocks in accordance with their functional logic or operational relationship. Therefore, a complex system becomes intuitive and easy to build and read in the form of RBD. However, RBD is only used for non-repairable systems.
Because of this limitation, the ExtendSim Reliability module has achieved the application of RBD for both repairable and non-repairable systems. With ExtendSim, a reliability model is built by different functional blocks stored in the Reliability Library. In addition to its intuitive and user-friendly advantage, the ExtendSim RBD can simulate the maintenance process in complex systems. By applying the Monte Carlo method to repeat simulations thousands of times, the ExtendSim RBD model can provide accurate results of component reliability, the mean time to failure, and the operational reliability of both non-repairable and repairable systems.
Results and Conclusions
The RBD blocks developed by ExtendSim can quantify the operational reliability of the remotely controlled siphon system, successfully and efficiently. RBD as an efficient tool can decrease the difficulty of the modeling work, especially dealing with a complex system. Moreover, the powerful ExtendSim software can allow over 10,000 simulations to finish in a short time. Due to the flexibility and efficiency of ExtendSim software, the operational reliability of any complex system can be successfully evaluated.
Project Background
Since urban flooding is not an evitable natural hazard, this team proposed a method to release part of the water ahead of (e.g., a few hours or a couple of days before) a heavy rainfall that is forecasted to produce flooding. To make this approach possible, a siphon system is built which can be remotely operated. This siphon is wirelessly connected and can receive and perform orders from a Decision Support System.
Although there are many advanced hydraulic simulation software in the industrial market, none can perform highly customized function to perform siphon. However, ExtendSim has highly advantage of customized design. Such advantage can achieve the function that other hydraulic simulation software cannot achieve.
Multi-wetlands are cooperated with each other to perform like a system. Therefore, observing and understanding the dynamic change in the multi-wetland system is more important for the wetland manager to come out strategy. Results from this research will provide guidance for the 12 artificial wetlands which will be built in Texas, and further to provide management strategy for the whole cypress creek catchment with the coupling of Decision Support System.
Wood Drying Process in Sawmills
 Mapping and Simulation of the Wood Drying Process at VIDA Vislanda AB
Mapping and Simulation of the Wood Drying Process at VIDA Vislanda AB
Jacob Forsberg
Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences
Masters in Forest Science • June 2018
Abstract
 The market for wood products from sawmills is under hard competition both in Sweden and in the global market. To reach profitability, sawmills need to have an effective and solid process for production while maintaining high quality products. An important part of this is how well the drying process is being managed. The company in this study, Vida AB suffers from a lack of capacity in their drying process which forces them to dry the wood faster than recommended. There are two main reasons for that. First there is a lack of capacity in the kilns to dry all the sawn volumes and at some times, there is a lack of heat to dry all the sawn wood in an optimal way.
The market for wood products from sawmills is under hard competition both in Sweden and in the global market. To reach profitability, sawmills need to have an effective and solid process for production while maintaining high quality products. An important part of this is how well the drying process is being managed. The company in this study, Vida AB suffers from a lack of capacity in their drying process which forces them to dry the wood faster than recommended. There are two main reasons for that. First there is a lack of capacity in the kilns to dry all the sawn volumes and at some times, there is a lack of heat to dry all the sawn wood in an optimal way.
A fast drying process will most likely lead to damaged wood and a lower quality. To improve the drying process we investigated how different scenarios affect the process. For example:
- What happens if we add a higher amount of capacity to the system?
- What happens if the production of wood in the sawmill increases or decreases during different parts of the year?
The aim of this study was to map the logistics connected to the drying process and use that data to construct a simulation model that represents the drying process at Vida Vislanda AB. Further, the model would be used to simulate 5 scenarios and examine how various factors affect the drying process according to dried volume, average volume in the inventory, and average waiting time for an m3sv in the inventory.
The method used was discrete event simulation and the simulation model was designed in the simulation software ExtendSim. The model was built with input data collected from the sawmill and it was verified and validated in several steps. The model gives three main results from the simulations, these are dried volume in m3sv, volume in the inventory in m3sv and average waiting time in days for an m3 saw wood in the inventory.
Approach
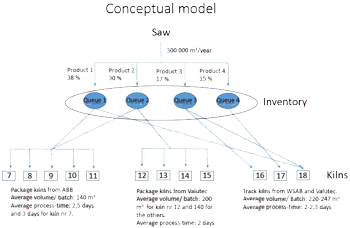 The study was done in six steps.
The study was done in six steps.
- A mapping of the drying process showing how it’s controlled and planned. This conceptual model shows the wood drying system at the sawmill.
- In cooperation with a supervisor and the head of the sawmill, 5 scenarios were investigated.
- Build a simulation model to represent the process.
- Validate the simulation model.
- Run the simulation.
- Analyze simulation results.
Results and Conclusions
The simulation model proved to work well for its purpose of representing the drying when the results were compared to historical data. The results from the scenario simulations provide several interesting insights about how different conditions affect the models results. Among other things, they showed that a production increase to 300 000 m3sv would be manageable, but 310,000 and 320,000 m3sv would result in high inventory levels and long waiting times. Other results show that a new kiln would have a major positive effect on the drying process.
Project Background
There had been very little research done on the wood drying process in sawmills in the past. The research that has been done both in Sweden and in other countries mainly focuses on the technical aspects of the process and how various techniques affect the wood quality. The author hadn't found any research that uses simulation for the drying process. Using simulation has been done with good results in the sawmill area before by Dogan, McClain and Wicklund in 1997 in their study "Simulation modeling and analysis of a hardwood sawmill". But that study just focused on the sawing process, not the drying. And the fact that no research has been done with simulation in this area makes this project unique.
Other Publications
In previous years, many students in the Department of Forest Biomaterials and Technology here at the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences have used ExtendSim in their theses with good results. Here a just a few of them:
Sofia Wahlström Bergstedt and Elin Kollberg. "Simulation of queueing times for an alternative unloading solution at the integrated mill in Iggesund". Bachelor thesis, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences. 2014.
Oskar Gustavsson. "Simulation of combined transports and mapping of the effects on service dimensions". Master Thesis, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences. 2015.
Anders Eriksson. "Improving the efficiency of forest fuel supply chains". Doctoral thesis no. 2016:101, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences. 2016.
Petter Berggren and Philip Öhrman. "Forest felling comparison between conventional two-machine systems and one-machine systems". Bachelor thesis (report under production), Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences. 2017.


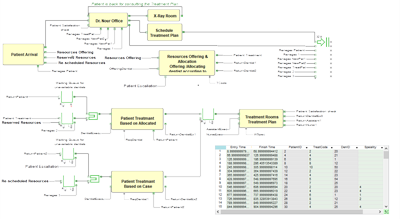
 Prezi presentation
Prezi presentation FAIM Conference 2010
FAIM Conference 2010